How AI and Digital Transformation Are Connected
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the field of study dedicated to creating “intelligent” machines. Applied to the field of business, this intelligence is central to digital transformation (DX), a process that involves transforming all activities and operations of an organization.
The intelligence in artificial intelligence refers to human-like capabilities such as reasoning, problem-solving, language learning, logic, analysis, or recognizing patterns. These skills allow machines to mimic human thinking. AI tasks can be mundane (such as perceiving and describing a painting, or translating a text), formal (such as assisting with project management and resource allocation or solving a Rubik’s Cube), or expert (such as detecting cybersecurity threats or powering self-driving cars).
Digital transformation fundamentally changes how an organization operates and delivers value, going beyond simply converting analog information and processes to digital formats. It involves a comprehensive overhaul of the organization’s core processes, workflows, and customer experience management. By integrating technology across all products, operations, and functions, digital transformation reshapes the entire business landscape.
“This journey of ‘digitization’ is 100 years old,” says Prasad Akella, Founder of Drishti, an AI video analysis company. “There’s a morphing process that occurs, and digitization in each generation changes colors. But it goes back to the idea that you're trying to automate a lot more, and there’s less human work going in. In the United States 100 years ago, 80 percent of the population was involved in agriculture. Today less than 10 percent is. That’s because mechanization was the first form of digitization.”
Digital transformation itself is always transforming. The current iteration of it is about more than mechanization; it’s about the integration of technology into all aspects of the company’s functioning and operation, which also means bringing about fundamental changes in the overall culture. Its effects can be seen in the relationship of the company to its own data and in the ways employees work individually, teams work together, and business processes work overall.
Every company is different, so each will have a slightly different roadmap to digital transformation based on its individual needs and goals. But all successful digital transformations have one element in common: They revolve around customer experience.
But what do we mean when we talk about transformation? “Companies are changing their basic offering and the product itself,” says Mahesh Makhija, Partner and Consultant at EY India. “Take a company like a bank — at one time a bank used to be a place where you’d go with your personal money or to get a loan. But now, using digital and using analytics, they offer you a full experience. If you’re a consumer, you're getting almost an e-commerce experience. The mortgage arm is helping them actually locate a house. You’re going beyond your core offering and understanding the customer’s needs and building a whole bunch of new products and services to be able to cater to that customer.”
In the case of a small business client, a bank would traditionally be approached by the small business for a small business loan. But now, says Makhija, “the bank will help them all the way, from acquiring laptops, doing procurement, helping them with tax filings and payroll… This is all from a bank. The bank itself is offering all these services in an attempt to get and retain more customers. That’s what is happening from a digital transformation perspective.”
The four dimensions of digital transformation are technologies, activities, boundaries, and goals. According to a paper on the “AI readiness framework” published in the journal Business Horizons, these are the four broad dimensions of organizational life and culture, and therefore the four broad areas in which an organization can undergo transformation:
- Technologies: New digital technologies are an inherent requirement of digital transformation; they in turn shape the organization’s activities, boundaries, and goals.
- Activities: Technologies can influence what actions in an organization can be optimized, augmented, or completely transformed, affecting the tasks assigned and the skills required. Learning algorithms, for instance, can fundamentally change the nature of expertise in an organization, reshaping occupational boundaries.
- Boundaries: Many types of boundaries can shift in an organization with the introduction of digital technologies: physical products are enhanced with digital components, physical workspaces are increasingly replaced with remote workspaces, skills are significantly replaced, and an organization’s entire relationship with its customers changes.
- Goals: Digital transformation involves creating new processes, products, and — ultimately — new goals; it has a profound impact on an organization’s identity. This is brought about by new digital technologies.
| Dimension of Digital Transformation | Manifested in… |
|---|---|
| Technologies | Changes in digital technology |
| Activities | Changes in activities, triggered by changes in digital technology |
| Boundaries | Changes in boundaries, triggered by changes in digital technology |
| Goals | Changes in goals, triggered by changes in digital technology |
You can use these four dimensions of digital technology to evaluate the current situation and capacity, as well as future expectations and needs in an organization. This helps leaders know what their employees are confident about and where they are unsure.
Surveys cited in the California Management Review found that 85 percent of organizations reported plans to implement AI in 2016–2017, and 20 percent of organizations reported already having done so. According to a report by Research and Markets from earlier this year, the artificial intelligence market is expected to have grown at a compound annual growth rate of 52 percent during the period from 2017 to 2025.
“AI acts as a catalyst for digital transformation initiatives across industries,” says Babu George, Editor of Digital Transformation in Business and Society: Theory and Cases. “With its ability to process vast amounts of data, automate processes, and generate insights, AI will underpin technologies driving the digital wave. Conversely, the data deluge from digital transformation fuels AI development, creating a virtuous cycle.”
How Is AI Different from Automation?
Both AI and automation help businesses operate more efficiently, reducing costs, carrying out tasks faster and more accurately, and leveraging data more effectively. However, AI involves systems that can learn, make decisions, and adapt over time, whereas automation refers to technology programmed to perform repetitive tasks consistently.
Here are some key ways that AI and automation differ:
- Nature of Process: Automation refers to the process of creating hardware or software that can perform tasks without human intervention. Artificial intelligence is the science of creating technology that can try and match or even compete with human intelligence and behavior.
- Amount of Data: Automation operates with a finite set of clearly defined data, as these machines follow fixed programming to perform tasks mechanically. In contrast, AI requires much vaster quantities of data to function and can handle a little bit of uncertainty, similar to the human brain.
- Type of Thinking: Automated systems use a fixed, linear set of steps when they perform tasks. AI systems attempt to mimic human thinking and reasoning, so they respond to and recognize more complex patterns of information. AI uses many technologies to process enormous data sets quickly through mathematical analysis or logical reasoning, and then attempts to make decisions or predictions.
- Required Supervision: Automated systems are meant to reduce human labor with repetitive tasks and shouldn’t require supervision. AI has to be more collaborative, especially when initially introduced into an organization or workflow.
- Purpose of Labor: Automation is about repetitive tasks; it does not involve the machine learning new processes or having to think for itself. On the other hand, AI systems are capable of adapting to new circumstances, learning from data and experience, responding contextually, and improving over time. They can handle complex and unstructured tasks that might require contextual understanding and reasoning.
AI versus Automation
| AI | Automation | |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Work | AI mimics human intelligence. | Automated systems perform tasks automatically. |
| Quantity of Data | It requires vast quantities of data and involves some uncertainty. | They can work with finite information and require clear programming. |
| Type of Thinking | It can recognize patterns, reason, and make decisions and predictions. | They follow a fixed, linear set of steps repeatedly. |
| Required Supervision | It requires collaboration. | They should not require collaboration, which saves the time required to supervise. |
| Purpose of Labor | It learns from experience, adapts to new circumstances, and responds to context. | They repeat the same set of tasks. |
Why Is AI Important to Digital Transformation?
As businesses continue to adjust to the changing digital landscape and the artificial intelligence industry grows, AI is becoming crucial to successful digital transformation strategies. Adopting AI can improve profitability and customer experience and enhance business leaders’ decision-making capabilities.
“AI has already become critical for digital transformation in the near future due to its ability to augment human capabilities across the value chain,” says George. “Key benefits include hyper-automation reducing costs, advanced analytics for smarter decisions, and intelligent process automation enhancing productivity. Moreover, AI enables innovative business models such as predictive maintenance, dynamic pricing, and hyper-personalization — ultimately translating to higher profitability and competitive advantages.”
- Better Analytics: AI enables organizations to process more data faster, helping them see new connections and patterns and make better predictions. For example, when supervised appropriately, AI can aid healthcare analytics companies to identify new groups of at-risk patients; similarly, a marketing company might benefit from AI’s analysis of website e-commerce data to better target its campaigns.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By processing more data faster, AI empowers organizations to make more informed decisions based on patterns it identifies and connections it makes. This in turn provides businesses with actionable insights they can use to stay flexible and adaptive. For example, a financial management company might use AI to discern new opportunities and risks, then take that information to better advise clients.
- Increased Profitability: From reducing costs to cutting waste, AI can help improve profit margins by optimizing processes and improving logistics. For example, a manufacturing company might utilize AI to help with maintenance of equipment, or a car or hotel service could use it to help with dynamic pricing.
- Enhanced Customer Profile: Using more data, AI can help build clearer and more detailed client profiles that businesses can use to understand their customer needs better. A bank, for example, might use AI to analyze spending patterns and help design personalized offers, such as specific loans or portfolios.
- Improved Customer Experience: AI can also help companies improve overall customer experience. More traditional businesses and systems will have a fixed amount of knowledge and use cases from which to learn, while AI can help predict problems that customers haven’t faced yet.
Use Cases of AI and Digital Transformation
AI can be creatively adapted for any number of business purposes. Different industries are likely to use different types of AI solutions for different reasons, but most solutions can be applied across industries.
Below are some real-life use cases of AI being deployed by companies:
Customer Experience: AI-powered engines can use data about customers’ purchases, inquiries, social media activity, and location to help companies tailor their offerings and recommendations. For example, Booking.com uses machine learning models to provide customers with targeted recommendations for hotels and flights based on their activity, and its AI Trip Planner answers customers’ queries as they plan their own travels. Erica, Bank of America’s virtual assistant, provides financial advice to customers and helps them seamlessly perform transactions.
- Fraud Prevention: Fraud prevention often requires processing large amounts of data quickly and recognizing patterns in order to identify anomalies, making AI a powerful tool for the job. A 2021 IBM study found that security automation and AI saved companies significant breach costs. Those that didn’t use AI paid more than twice the amount paid by those that did. The market for fraud analytics is expanding rapidly, almost doubling between 2021 and 2023. PayPal uses AI tools to analyze transaction data and assign a risk score for every transaction in order to differentiate between legitimate and fraudulent.
- Generative Design: AI technology can generate numerous product design options using fixed parameters and advanced algorithms to help engineers, designers, and architects develop their products more quickly from immediately available prototypes. For example, the aircraft manufacturer Airbus used generative design to create a “bionic partition” structure that could help reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
- Robotic Process Automation: Robotic process automation (RPA) can make companies more efficient and streamlined by automating their routine tasks and manual workflows, reducing pressure on employees. For example, IBM has used RPA extensively in its HR department; during the onboarding process, RPA software carries out all document scanning and validation and conducts basic data entry on new employees. This frees up HR staff to concentrate on more strategic initiatives, such as employee engagement. Insurance companies are another example; by using RPA and data analytics, these companies can validate and quickly process the information in claims forms, improving customer satisfaction.
- Sentiment Analysis: Natural language processing (NLP) can help systems analyze customer interactions and gain insight into their context and emotional background to help with sales and marketing campaigns. User sentiment analysis involves understanding the thinking and emotional motivation behind the things your audience says in public and turning this analysis into action items. For example, Amazon uses sentiment analysis of customer reviews to gauge overall satisfaction and improve product recommendations.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI helps businesses plan and optimize their logistics and manage their supply chain. A 2021 study by McKinsey found that supply-chain management powered by AI has improved logistics costs by 15 percent, inventory levels by 35 percent, and service levels by 65 percent in companies that adopted early compared with companies that were slower to adopt. One example of AI-powered supply chain management is UPS’s logistics platform ORION (On-Road Integrated Optimization and Navigation), which maps out the majority of the company’s domestic routes and helps resolve problems with vehicle routing and scheduling. ORION uses machine learning algorithms to analyze traffic patterns, weather conditions, and other real-time information to generate optimized delivery routes for UPS drivers.
AI Digital Transformation Case Study
There are endless ways AI can be adapted to a specific organization to further its digital transformation journey. Digital transformation is happening everywhere around us, all the time. Here is one team’s story.
Kelly Cheng is the head of marketing at Goldcast, a B2B events platform that helps companies host webinars, virtual summits, and all manner of hybrid events. According to Cheng, AI has fundamentally changed the way her team works and has saved them time. This is crucial at a moment like this, she says, when layoffs are widespread and companies everywhere are finding themselves unable to sustain the revenue or pipeline they’re creating.
“There’s been a massive shift in terms of needing efficiency,” she says, “but that’s very conflicting with marketing work because marketing work is creative. It’s not efficient work.” It can take months to create some of the material that marketing teams such as Cheng’s are pushing themselves to create, but teams everywhere are finding themselves without enough time or resources.
This is where AI comes in. “AI can serve marketers as a really effective tool for brainstorming ideas,” Cheng says. “Marketing is one of those things that will never really truly be replaced by robots because you have that original thought and you have to be authentic for it to be effective. But how marketing can leverage AI to really help them do more with less is really with the brainstorming side.”
At Goldcast, teams use AI tools to help come up with event or webinar topics. Then Goldcast sets up the event, and the end product is in video format. This is the original material that Cheng’s team uses to create their marketing content. With the current resource limitations, Cheng’s team leans on AI to help them find marketing ideas within their recorded events quickly. “You have the original, authentic video — a live webinar or a thought leadership panel that you’ve captured — but no one’s really going to sit there and watch 60 minutes of video,” Cheng says. “The way that people consume content now is very snackable.”
Creating TikTok- or Instagram-style content from such heavy source material would take a lot of resources if working solely with a video editor; that would mean repeatedly watching long webinars to find the right moments to use. Also, as Cheng points out, “the video editor isn’t your subject matter expert. They don’t know what parts to cut and which part your audience is gonna really, really love.” That’s the marketing team’s expertise.
At Goldcast, all content — webinars, events, internal meetings, Zoom recordings, and product demos — is moved to a designated content lab. Next, its AI program generates a transcript of every recording, and then “the world is yours,” Cheng says. (Our call was recorded on her program, and the transcript generated required minimal editing from either of us.) You’ve saved yourself hundreds of hours using the help of an AI that has identified for you the five key moments in an hour-long meeting or panel.
Goldcast’s specific program also cuts and creates five key video clips that can be used to engage with consumers: people who may have been in the audience at the event, who may have missed the event or wanted a summary, or who are simply scrolling on LinkedIn. “Creating short-form videos from long-form videos means you can do more with less, and it really extends the shelf life of that long-form video,” Cheng says. “You can really extend your audience that way.”
The company’s Content Lab can be prompted to generate specific output as well: writing text for a LinkedIn post to accompany a specific video, creating an outline for an SEO-driven article about an event, sending a follow-up email to the attendees of a specific webinar, or creating summaries or writing FAQs after internal meetings.
“We’re thinking through how we can continue to apply AI to the platform to make it more functional and more efficient for the marketing teams to use,” Cheng says. “But this is live. This is fully in product and people are paying for it.”
For businesses and teams looking to adopt AI tools for their digital transformation journey, Cheng recommends simply diving in. “My tip is just to get started, start creating and start using and testing and experimenting and seeing what works,” she says. “Keep experimenting until you have something that can go live. This is a very early market. There’s a lot of innovations still happening. If you want to really find those benefits of efficiency, of being more creative, you have to start now. Otherwise, it would take a long time for our teams to catch up with the technologies out there.”
How to Use AI to Help Your Organization's Digital Transformation
When rolling out a new AI system in your organization, make sure you have all the information you need and gather as many resources as possible. Then, define specific use cases, build cross-functional teams, and develop, train, and integrate AI models into existing systems.
Follow these steps to aid digital transformation using AI:
- Identify Objectives and Challenges
Start by identifying the specific objectives you want to address with AI, and the challenges you want to use it to solve. This could be driving change and innovation to help your organization move into new areas or helping business-as-usual with improved operational efficiency.
- Evaluate Data Readiness
AI systems can’t work without the right quantity and quality of data. Before you can implement any new AI systems, make sure that the data infrastructure you have in place can support them. If it can’t, start by increasing your data collection and integration.
- Define Use Cases
Focus on specific projects where AI’s impact and value can be maximized, keeping in mind your organizational goals.
- Build Cross-Functional Teams
Successfully implementing new AI tools in your organization requires collaboration. Build teams that include different kinds of experts, including data scientists, developers, analysts, and IT infrastructure specialists. Introducing AI tools also requires specialists, such as change management experts and compliance officers. This keeps your AI initiatives focused and always aligned with your business objectives.
- Develop an AI Model
Depending on your specific needs and data, choose an AI model to build on. Here are some broad examples of what models might add value to your organization:
- Deep Learning Model: This is a type of machine learning that requires much more data and computational resources to perform. Deep learning models are responsible for natural language processing, which is responsible for chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Machine Learning Model: This type of model might help gain insights from data or automate processes. It would enhance tasks such as trend forecasting, customer segmentation for marketing campaigns, or analyzing simple videos for quality control.
- Symbolic AI Model: This model learns directly from human expertise rather than data; it follows rules that are programmed into the system by real experts. For example, these systems might be used for image analysis in medical fields to help diagnosticians.
- Train Your AI Model
Once you’ve decided on your AI model, train it to address the specific use cases identified earlier, and run a test in order to evaluate it. Make adjustments as needed.
- Integrate with Existing Systems
Integrate your new AI solution with your current workflows and applications to enable smooth adoption. This may involve developing APIs, connectors, or custom integrations. Then, run your pilot implementation in an actual use case to assess the solution’s effectiveness and user-friendliness. Collect feedback from all stakeholders, including employees and end-users.
- Monitor Performance
Continuously monitor the performance of your AI models, and use feedback to refine them over time. Implement mechanisms for tracking key metrics, detecting anomalies, and retraining models as necessary to maintain their accuracy and relevance.
- Scale Across the Organization
Once the pilot phase succeeds, you can expand your AI solutions to different departments or teams. Consider each department’s initiatives and requirements, and lay out a roadmap for the scaling process
- Invest in Talent
The long-term need for any organization implementing AI into their business is a workforce that’s trained with the right skills and knowledge. Consider building internal capabilities on an ongoing basis in fields such as data science and AI to ensure that your organization has the resources and expertise required to drive digital transformation in the future.
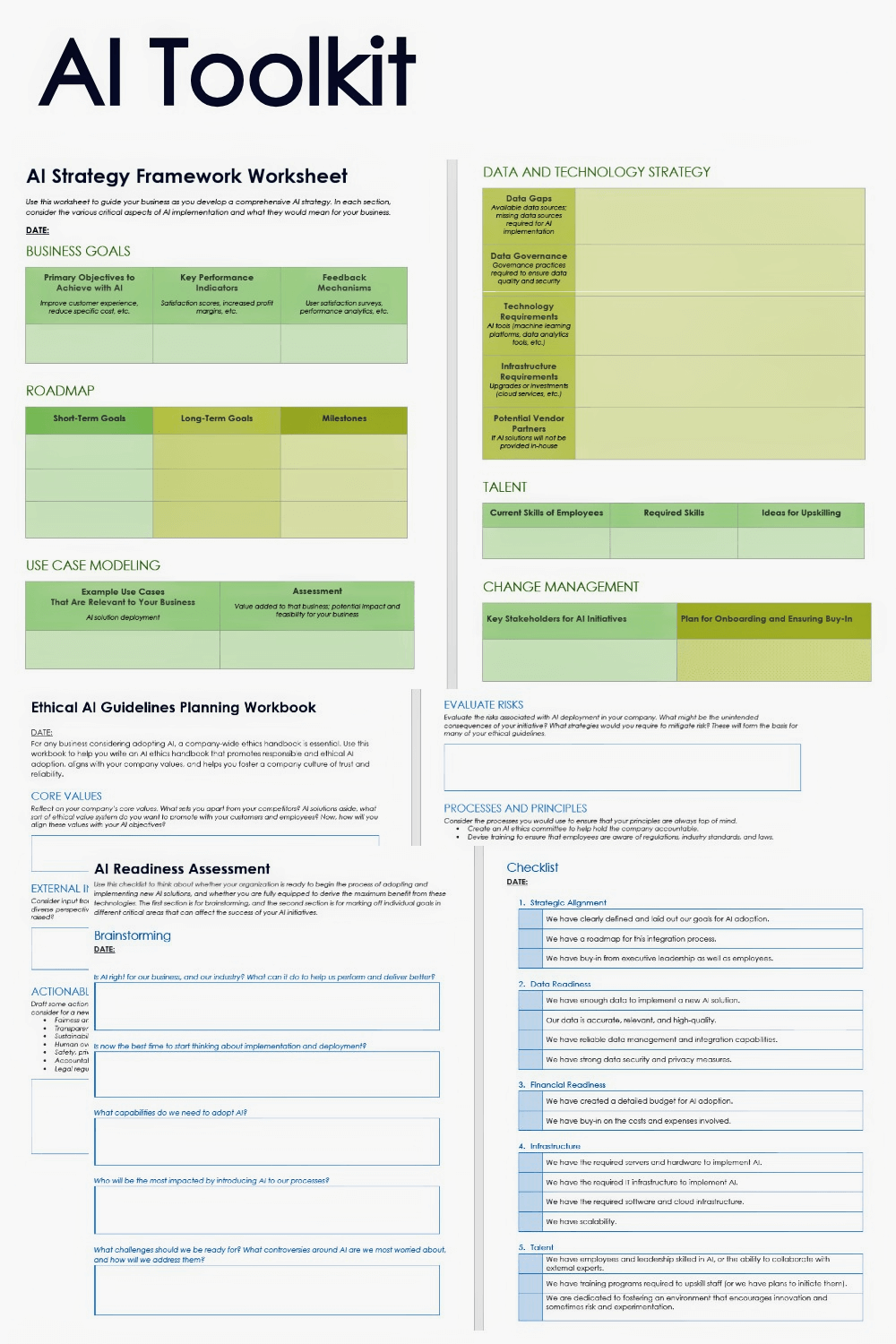
AI Toolkit
Use the resources in this free AI toolkit to help you get started with the AI adoption process. The kit includes detailed guides for assessing your AI readiness, strategy, and ethics.
In this kit, you’ll find…
- An AI strategy framework worksheet for Microsoft Word to create your own guidelines and best practices that align your AI strategy with your business objectives.
- An AI readiness assessment for Microsoft Word to help you assess your organization’s readiness for AI adoption, considering factors such as data infrastructure, talent, compliance, and others. It includes a worksheet to help you brainstorm some kickstarter questions and a checklist.
- An ethical AI guidelines planning workbook for Microsoft Word to help you draft your own guidelines for your company handbook, ensuring that you engage in ethical and responsible AI development and integration.
Expert Advice for Using AI for Digital Transformation
The most important thing to remember is that investing in your organization’s digital transformation is always an ongoing process, and introducing AI may not be a one-time event. Be open to experimentation, stay agile, keep in touch with emerging trends and technologies, and encourage a culture in your organization that strives for continuous improvement in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Elias Hayek is an independent management and strategy consultant and a former business instructor at Algonquin College. In his article, “A Leader’s Framework for AI Application in Business,” he identifies what he calls the “AI kickstarter wheel,” which begins with the first round of questions and concerns that business leaders should raise when considering implementing AI:
- What can AI do to help us innovate, outcompete, and improve business performance?
- Is AI even good for our business and industry?What capabilities do we need for this type of project?
- How and where should we start? Is now a good time to deploy AI?
- How much do we need to invest and how to justify ROI?
- What is the impact on our organization? Who will be impacted?
- What are the expected challenges given the controversies around AI?
To organize these concerns and to help business leaders foresee challenges and brainstorm solutions, Hayek devised the “triple S framework.” Using the principles of scope, strategy, and structure, AI deployment can be smooth and successful.
“From my own experience, two major problems surface when it comes to AI deployment in organizations,” Hayek told Smartsheet. “The first one is related to the misunderstanding of the use of the technology by midlevel managers. Now, sometimes these people are familiar with AI applications, but they either lack proper training or they fail to see the benefits of using AI in their day-to-day jobs. These people are usually the drivers for change, and that’s where many digital transformation projects hit a roadblock. The second challenge is related to a strategy development gap at the top level. Many leaders want to deploy AI in their organizations but do not really understand how to create value with AI. They misunderstand the technology — maybe because it’s trendy and everybody wants to join in — and ultimately they end up drafting digital transformation strategies that do not really have a scope or purpose. AI remains a buzzword in the office with no real application.”
Hayek’s advice to counter these potential problems is to “address these challenges before even thinking about AI adoption.” This is where the “triple S framework” comes in. “Scope helps leaders from all levels of the organization come together and brainstorm the best AI solution in their particular case. In other words, what do they actually want AI to achieve for their organization?” Hayek says. “From there, leaders move on to develop a strategy that matches organizational objectives. Once the objectives and strategy are clear, structure of the execution comes last. With midlevel managers involved in the entire process, adoption is easier and the change happens faster.”
How to Implement AI for Your Organization’s Digital Transformation
Implementing AI is the first and most important investment for your digital transformation journey. AI can help in almost every aspect of your business, but it also requires collaboration, maintenance, and communication.
As you can learn in this downloadable guide to digital transformation, overhauling a company’s digital operations requires planned, strategic action. Once you decide to invest in AI for digital transformation, keep in mind the importance of these key steps:
- Defining the Problem: This is the most important step before implementing an AI system. It’s critical to clearly define what problem the AI is solving. What are you trying to achieve, and what will the AI do to help you achieve it? It’s also important to decide on your evaluation system at the beginning. Before you start implementing, know what factors or metrics you’ll use to make your assessment of the AI system.
- Training and Collaborating: Business leaders are responsible for ensuring that employees are comfortable with any AI system that’s being implemented and for showing teams how they can successfully incorporate AI into their departments and work processes. This involves determining which roles will be affected by AI and how, as well as ensuring that everyone is trained and upskilled as required.
- Encouraging Innovation: Part of ensuring that employees are comfortable with new AI systems is creating room for them to share ideas and explore as they discover new details and get to know the technology. Collaboration across departments can build bridges and ultimately improve everyone’s efficiency and drive. It’s not only processes and workflows that are undergoing transformation in your organization; your people and their perspectives are, too.
- Integration: An effective AI implementation strategy always considers how to integrate new systems with systems that are already in place. This process should be as smooth as possible, avoiding disruption and improving productivity. All employees who have to use the new system should be on the same page.
Organizations can harness AI for digital transformation in various ways. Here are a few of the roles it can help improve in your organization:
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants can offer personalized care and recommendations to customers, improving engagement and loyalty. AI can also be used to analyze customer behavior and feedback and carry out sentiment analysis to better understand their preferences. Additionally, AI’s ability to help with tasks — from automated ticket routing to multilingual support — makes it easier to connect customers with the right department or officer, enhancing their overall experience.
- Finance and Accounting: AI can automate routine financial tasks such as data entry, bookkeeping, invoicing, expense management, and reconciliation; chatbots and virtual assistants can also help address financial queries or concerns from clients or employees, and some AI tools specialize in detecting fraudulent or anomalous transactions. Predictive modeling and data analytics can streamline budgeting and forecasting as well.
- Human Resources: From job posting, recruiting, and screening to onboarding and supervision, AI can automate HR processes to allow employees to spend more time thinking about talent critically. This could involve building engagement, filling skill gaps, and conducting workforce analysis.
- Marketing and Sales: As Goldcast shows, AI can streamline and improve the marketing and sales process in many ways. It can assist in carrying out market research, analyzing customer data, predicting trends, forecasting sales, creating personalized messaging, condensing large amounts of content into manageable portions, and much more.
- Operations: AI can streamline and optimize internal processes across departments. To improve an organization’s operations, AI can reduce costs by improving processes such as data entry, maintenance scheduling, document processing, and quality control. AI tools also help manage and evaluate workforce, and optimize logistics to minimize transportation costs, and monitoring inventory.
- Product Development: AI systems can help generate or inspire new ideas through research and predictions of demand and new trends. They can also accelerate the product development lifecycle by improving design and prototyping.
- Research and Development: AI can help analyze large datasets and forecast outcomes for different business decisions based on predictive modeling. This can help uncover actionable insights, trends, and patterns, as well as inform strategic planning, risk management, and market intelligence. AI can also be used to design and conduct experiments automatically, adjusting its analysis in real time based on results.
- Risk Management and Compliance: AI’s predictive capabilities allow it to effectively detect and forecast risks and volatility, as well as ensure compliance. Some tools can model risk scenarios to help businesses understand the impact of different events.
Fast-Track Your AI Digital Transformation with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.