What Are Project Success Criteria?
Project success criteria are principles or standards that define what you need to accomplish in measurable terms to satisfy clients, stakeholders, and end users. The standards are variable and dependent, and they determine how you evaluate a project’s success.
Project success criteria have changed in project management practice. In past decades, budget, scope, and schedule were the guiding criteria. Today, strategic criteria — which are harder to quantify — also inform projects.
Project Success Criteria vs. Project Success Factors
Project success criteria center on results and outcomes. In contrast, project success factors are the independent activities or elements needed to achieve project criteria.
Success factors relate to project quality. Success criteria are about longer-term outcomes related to project excellence. In the research study by Collins and Baccarini, “Project Success - A Survey,” the authors note, "It is important to differentiate between success criteria and success factors. Criteria measure success while factors facilitate the achievement of success.”
Learn more about project success factors and tips for using them in your next project.
Project Success Criteria vs. Project Objectives
Project success criteria provide a directional framework for project objectives, which are the key steps and milestones to take to complete the project. They state desired results, including goals and deliverables.
Learn how to write project objectives that are specific and measurable, as well as identify time, budget, and quality constraints.
What Are the Main Success Criteria for Projects?
Main project success criteria include the classic iron triangle: cost, time, and scope. In addition, stakeholder satisfaction, team satisfaction, resource utilization, control, risk management, and quality are also vital project criteria categories.
Jon Quigley, Principal and Founding Member of Value Transformation, notes that the iron triangle of triple constraints is a central element that drives successful project execution and is weighed carefully: “Like everything in projects and project management, prioritizing objectives is a thoughtful balance of trade-offs. The cost, schedule, and scope most often influence balance. For example, the more prized the scope, the more the organization might consider adjusting the cost and schedule for effective success criteria project management. Say the profit margins on a project effort are high enough and the market large enough — there may be a willingness to enlarge cost and time parameters.”
“Original” Iron Triangle Project Success Criteria
- Cost: Containing costs and meeting budgets are critical success criteria for any project.
- Time: Most projects are time-based and must be completed in a specific time frame to conserve resources and meet business and competitive needs.
- Scope: A detailed written project outline, including timeline, budget, assigned tasks, project stakeholders, and workflow strategies, describes the project scope for stakeholders and team members. Following the project plan prevents overwork, misuse of resources, and detailed oversight.
More Project Success Criteria
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Satisfied stakeholders support company decisions and make it easier to deploy long-term strategies, work as a team, and obtain funding.
- Team Satisfaction: Satisfied work groups perform more efficiently and harmoniously. In addition, job satisfaction provides employees a sense of accomplishment and improves retention.
- Risk Management: Minimizing any event that might negatively affect projects prevents injury, financial loss, reputational damage, safety issues, and loss of intellectual property.
- Resource Utilization: The wise use of human, technological, and other resources saves time and money, and it frees up assets to move on to other projects faster.
- Quality: Producing the best possible outcome makes sense for every type of organization, no matter what product or service it provides. It improves relationships, sales, and brand reputation. For some companies, quality is critical because of safety factors.
- Control: Taking and maintaining control of every aspect of a project is fundamental to success. Shokri-Ghasabeh’s research, published in the “Generic Project Success and Project Management Success Criteria and Factors: Literature Review and Survey,” found that managers considered “project control” a primary success criterion. Documentation is crucial for managing and controlling every aspect of projects to the stated success criteria.
Hard and Soft Project Success Criteria
Hard and soft project success criteria usually both have a role in helping teams finish a project successfully. Hard criteria are quantitative and easier to measure. Soft criteria are qualitative and more subjective.
Project management criteria geared to success vary for the same project. “Hard success criteria refer to specific, measurable, and objective goals,” shares Value Transform’s Quigley. “Soft success criteria refer to more subjective or intangible goals that may not be as easily measured or quantified.”
Hard Project Success Criteria Examples
Examples of hard success criteria include meeting a deadline, staying within a specific budget, or achieving a level of performance or functionality. “The hard criteria are often associated with economics, the product, and the most important product features to be delivered,” advises Quigley.
Here are some examples of what is meant by hard project success criteria:
- Time: Must deliver on or before a specific date.
- Budget: Must not exceed a specified dollar amount.
- Scope: Control and monitor to prevent scope creep and deliver within the agreed scope.
- Financial Targets: Profit or revenue targets to meet.
- Web Activity: Increased website visitors.
Soft Project Success Criteria Examples
“Soft success criteria refer to more subjective or intangible goals that might not be as easily measured or quantified,” says Quigley.
Examples of soft project success criteria include the following:
- Top Management Support: The 2009 research report by Shokri-Ghasabeh found that “top management support was the most important factor by the survey respondents.”
- Customer Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction with your product or service is fundamental to success, which is often a criterion. Surveys or primary research measure satisfaction.
- Brand Perception: This is a goal for many companies. Brand perception is challenging to quantify, other than through consumer research.
- Innovation: Staying ahead of the competition is vital for companies, from technology to consumer goods, and can be a primary criterion.
- Media Mentions: Mentions in online media outlets or executive interviews is extremely valuable free advertising, particularly for companies introducing new products or services.
In his 2019 book “Project Management Methodologies, Governance and Success (Best Practices in Portfolio, Program, and Project Management),” Robert Joslin notes that success is subjective. He says, “Even with comprehensive definitions for success criteria for project management, some project criteria remain subjective by nature — for example, product usability or the acceptance of new processes. The methods and techniques aimed at quantifying subjective measures reduce subjectivity … Project success is a multidimensional construct in which project stakeholders can select several project success criteria they believe are important by which to judge success.”
How to Choose Project Success Criteria
Choosing project success criteria depends on your company and what you’re trying to achieve. Keep criteria realistic. Consider how the criteria align and further organizational goals as you explore options.
Project success criteria specifics vary widely. Müller and Turner's research paper, “The Influence of Project Managers on Project Success Criteria,” is based on 959 responses to a web survey. They found that the importance of project success criteria and success rates differed depending on the industry and project complexity.
Follow these steps when choosing project success criteria:
- Set Up the Team and Stakeholder Sponsors
Use a structured, collaborative process to develop and define success criteria. That way, all decision-making stakeholders can provide input, challenge assumptions, negotiate, and authorize acceptance. - Align to Organizational Goals
Keep the company's overarching vision, strategy, and goals in mind as you develop criteria. - Be Specific
Choose well-defined success criteria. State success criteria in specific terms tied to the execution of the project management process, project tasks, and related deliverables. - Get Buy-In
Quigley advises, “To achieve success, you need to agree with the stakeholders regarding the project goals, objectives, and success criteria.” The last criteria should be agreed upon between all the project's primary stakeholders (including the customer and vendors) and must be kept in mind throughout the entire project lifecycle. - Assign Responsibility
Depending on the size of the organization and team, designating a single person responsible for monitoring criteria progress may be sufficient. In larger organizations with more complicated projects, each criterion may have one person oversee measurement and monitoring. - Define Metrics
Soft criteria might be more challenging to measure, but they have a positive impact inside and outside of the organization. “Try to balance hard and soft criteria,” recommends Quigley.
How to Document Project Success Criteria
Use a spreadsheet or project management tool to document project success criteria. The key is to be on the same page and work toward the same standards. Document criteria before the project starts, and track activities continuously.
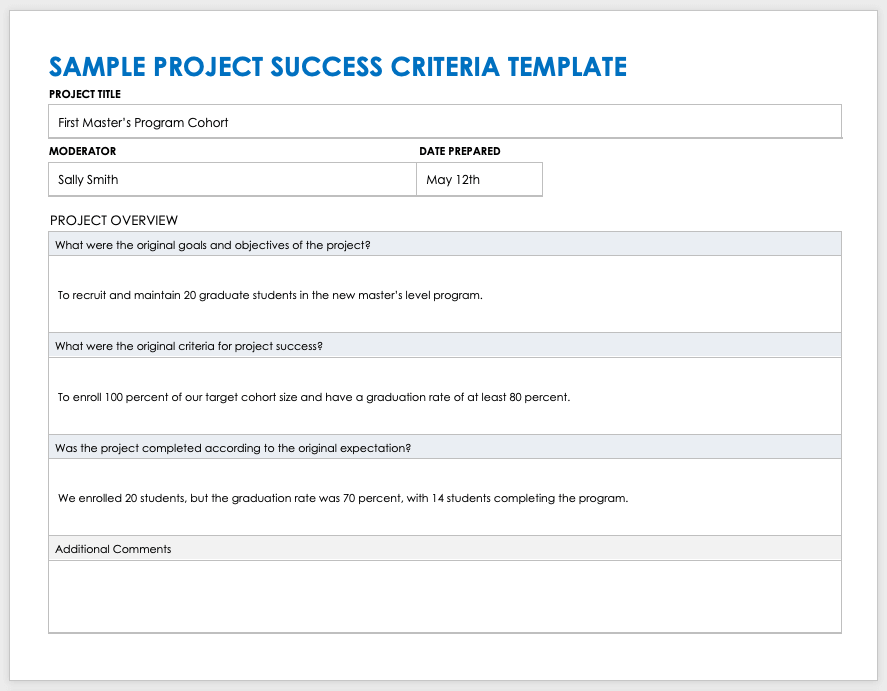
Project Success Criteria Template
Download a Sample Project Success Criteria Template for
Microsoft Word
|
Adobe PDF
| Google Docs
Project success criteria documentation and tracking are easier when using a template. The sample text in the template is completely customizable and serves as an example to help you start writing project success criteria. Use the template to document project success criteria, how and when you’ll measure progress, a responsible party, outcomes, and any issues and resolution. Once complete, communicate and share the documents with the team and stakeholders to keep everyone engaged and informed.
Find more project success templates in multiple formats.
How to Measure Project Success Criteria
The project team should decide how to measure project success criteria. Once you document your plans, review the project scope and specs. Share the documentation with stakeholders and team members. Analyze the budget. Review the client’s and team’s overall satisfaction.
Measuring quantitative and qualitative performance is vital to maintaining quality and learning what works for future projects. Read this guide on measuring project success criteria to learn how to apply it to your project.
Project Success Criteria Measurement Methods
Project success criteria measurement methods vary. Projects often use multiple methods to track metrics. Methods can be based on a scale or grade or use specific financial metric formulas.
- Graded: Once the criteria are written and approved, they can be graded using a number scale, from 1 to 10, to show success ranking.
- Weighting: Weigh each criterion for relative importance with graded measurement.
- Pass/Fail: The pass/fail approach shows whether the project met the criteria.
- Scale: Use a scale method to show achievement within a target range.
- Cost Benefit: A positive benefit is good, and a negative sign is terrible. The formula is the following:
Benefit = Benefit-Cost
- Return on Investment (ROI): Determine your return. The formula is the following:
ROI = [(Amount Gained - Amount Spent)/(Amount Spent)]*100
- Payback Period: The most accessible equation uses the payback period. Annual cash flows are unlikely to remain even across years. Instead, sum the various anticipated yearly cash flow. The formula is the following:
Payback Period = Total Investment/Annual Cash Flow
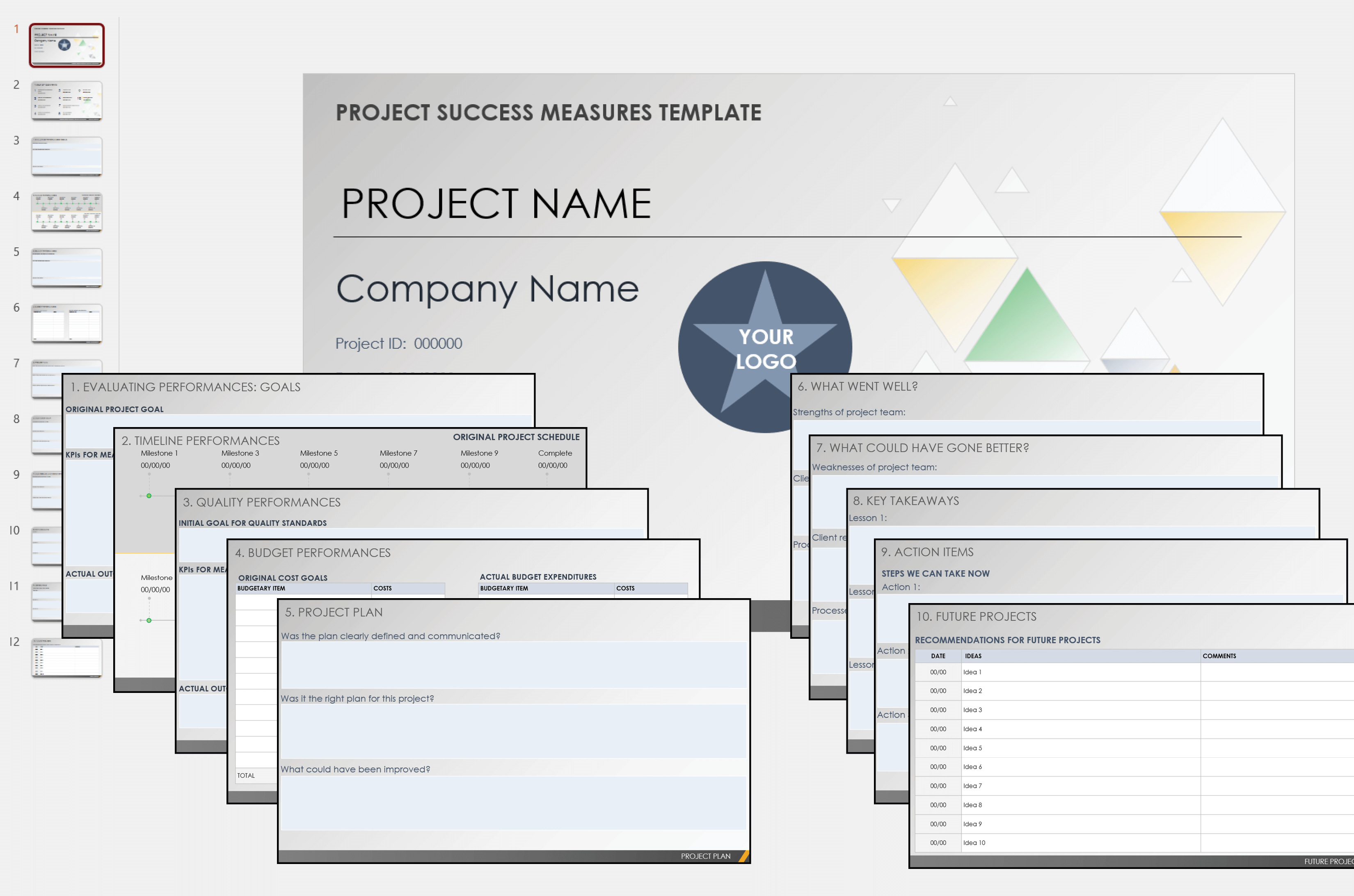
Project Success Measures Template
Download a Project Success Measures Template for
Microsoft PowerPoint
| Google Slides
This project success measures template helps you outline how you will quantify successes. Provide clear success criteria in the template to help ensure stakeholder and project sponsor buy-in. Customize the template by adding key performance indicators (KPIs) and plans for achieving success.
Find more project evaluation templates and checklists.
When to Track, Grade, and Weight Project Success Criteria
The cadence of when to track, grade, and weight project success criteria should be determined by the project team. Measure projects once complete to assess overall performance and inform new projects.
“Measurements are difficult – not just knowing what to measure, how to measure, or when to measure,” explains Value Transformation’s Quigley. “We can get information that helps, or we can be misled by what we see. It's important to set measurement standards and take the risks into account before you begin. Also, measurements are sometimes viewed as a mechanism for the punishment of the team members, so you need to explain that assessing with data is good for everyone and the project.”
Here are some of Quigley’s suggestions, based on decades in project management of large-scale manufacturing projects, on challenges and how to head off problems before they occur:
| Accuracy | Ensure precise measurements are accurate by deciding what tools and methods to use before the project begins. |
|---|---|
| Calibration | Calibrate measurement methods and tools regularly to maintain accuracy. |
| Complexity | Measuring complex structures or systems requires specialized tools and expertise. |
| Cost | Know the cost for equipment and tools required for accurate measurements and budget appropriately. |
| Environment | Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and lighting can influence measurements in production settings. Be aware and make adjustments accordingly. |
| Human Error | People taking measurements are prone to making mistakes, leading to inaccurate results. Train the responsible team members. |
| Standardization | Taking measurements in a consistent and standardized manner across a project is essential for accuracy. |
| Time | In fast-paced environments, measuring and recording data must be worked into schedules. |
Project Success Criteria Examples
Project success criteria examples exist in all types of business. Project success criteria were adopted early by technology companies, but industries such as construction and product development also adapted them as a best practice.
Agile Project Success Criteria Example
Taking advantage of success criteria as a best practice is a natural fit in Agile-based projects. Focusing on teamwork, collaboration, timeboxing tasks, and flexibility makes criteria different from traditional top-down or project manager-driven projects.
Seven common criteria in Agile are business value, customer satisfaction, work delivery, limiting project cost, commitment to specific deliverables, deliverable quality, team motivation, and satisfaction.
IT Project Success Criteria Example
IT projects are complex, and they operate with an intense focus on organization. IT projects are managed with an emphasis on six measurement areas: the developed system, the system's output, user satisfaction, system use, effect on behavior, and organizational performance.
Construction Project Success Criteria Example
The common success criteria for construction projects are the “traditional” time, cost, and scope. Quality, safety, client satisfaction, cash-flow management, profitability, and environmental concerns are common criteria for the industry. Team sizes, material costs, and strict deadlines mean that project managers use every tool possible.
In the Collins and Baccarin research paper on construction, “Project Success – A Survey,” they report, "It is significant that the most important success criterion was the product criterion of meeting the owner’s needs. This shows that the project management community is aware of the need to satisfy the customer ultimately. The significant implication is that the project management team must extract from the customer a clear and complete articulation of their requirements through rigorous scope and quality management processes.”
They add, “The research shows a positive relationship between project management and product success. This infers that the project management team must constantly monitor their project management performance (i.e., time, cost, and quality objectives) and reflect how this performance affects the achievement of product success.” The paper stresses the need for a long-term rather than a short-term perspective of construction project success.
New Product Project Success Criteria Example
Project success criteria help get new products off the ground. Criteria provide structure and discipline to simplify production and marketing efforts and clarify the path forward.
Quigley has managed many new product launches, from a car to software to aircraft. He notes that new product introduction must span hard and soft criteria because these are about brand and competitive factors, but there needs to be budget restraint. He explains the process:
“A project can sometimes be undertaken using 'strategic' criteria. In these instances, the business case is somewhat deferred or downplayed. The main objective is to get something new out into the market. Perhaps nobody is in the market yet, or the company is rushing to catch up to competitors in a market segment. The business case is less important than getting the company engaged in the market.
“There is a downside: we can get into a state where we keep putting money into the project with no tangible outcome. We spend large amounts of money and fall into the sunk cost fallacy. In this condition, we consider the lost money as being gone, and we restart the business case with the new expenditure. So we spent $500,000 and have not delivered the product, and the original business case built on this $500,000 is already gone. We need more funds, and we do our business analysis on the new expenditure estimate, say another $500,000. Now we are spending $1 million on the project objective. However, our business case will not include the total sum spent, only the latest allocation.”
“There is a balancing act to perform for these strategic projects. It is true that new products require learning and will cost time and money. However, it is possible to continue spending and not obtain the benefit. At what point has too much been put into this strategic project? How will we know? That’s where success criteria come into play.”
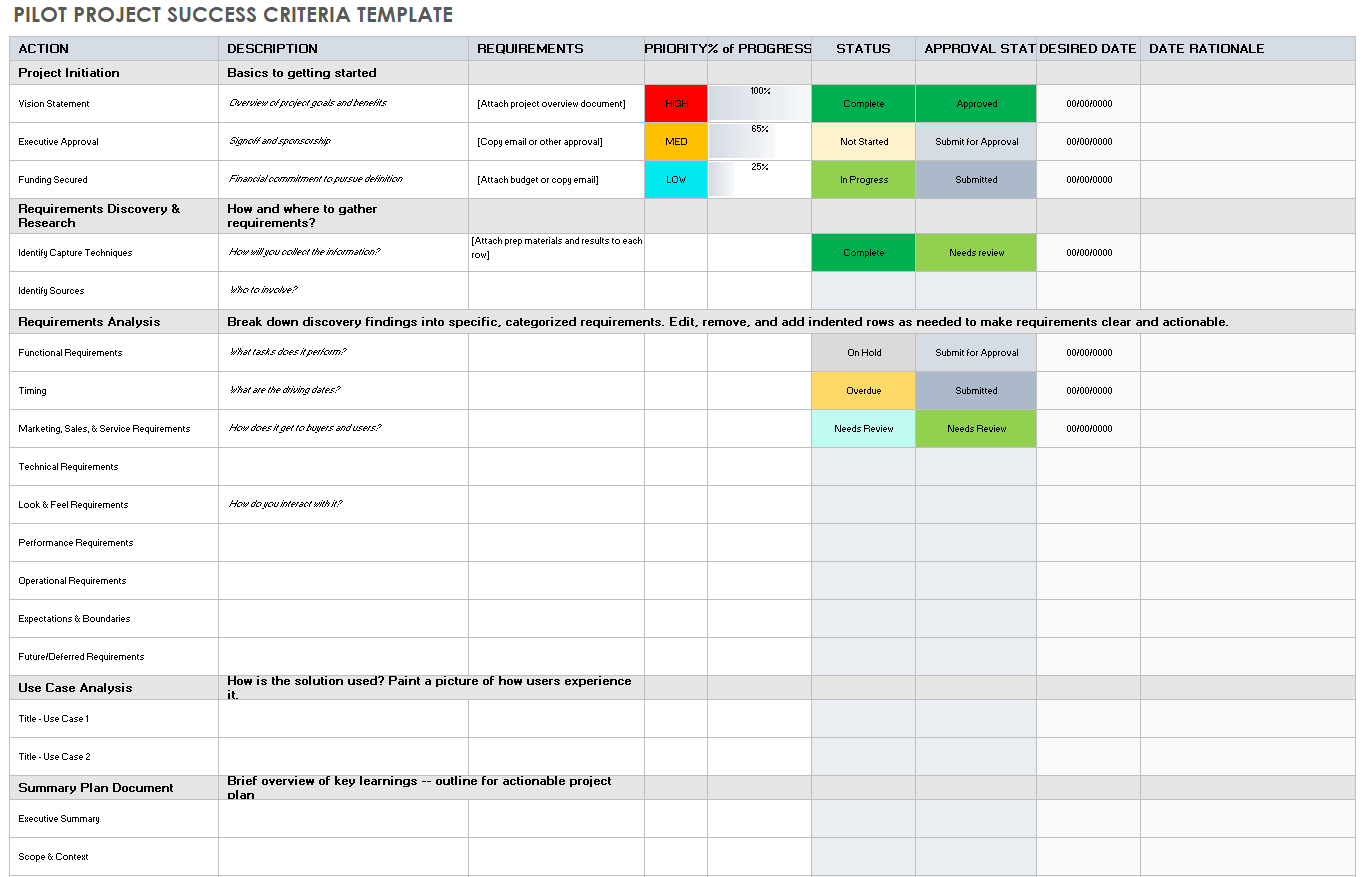
Pilot Project Success Criteria Template for Adobe PDF
Download the Pilot Project Success Criteria Template for Adobe PDF
This template provides ample space to document and share multiple aspects of pilot project success criteria beginning with project initiation. Insert how you will conduct discovery and research to gather requirements. Add details for requirements analysis and use case analysis, and provide user experience descriptions. Add a summary plan to wrap up everything you need to document as you prepare to launch.
Project Success Criteria Best Practices
To establish best practices in developing and applying project success criteria, start with taking time with your team to set clear criteria. Define documentation, keep it clear, and implement simple ways to track measurements.
- Select the Right Project: Knowing how to select a project that inherently supports the organization’s strategy is a must. Ensure management vets potential projects and weighs in on the product success criteria.
- Stick to What Matters Most: “Best practices depend upon the circumstances, constraints, and resources,” notes Quigley. “Generally, a good approach is to determine priorities and find ways to measure that while doing the work to ascertain trends.”
- Define Documentation: Establish the name of the success criteria and the measurement, as well as who will measure and who is responsible before the project starts.
- Never Forget: All stakeholders, including customers, should remember the success criteria throughout the entire project lifecycle.
- People Metrics Matter: Most people will act according to how they are measured, so the project success criteria will affect their focus during the lifecycle.
- Meet Regularly: Set periodic meetings in advance to measure the success during the lifecycle.
Challenges When Defining Project Success Criteria
Challenges are common when defining project success criteria. Beware of making criteria too narrow or ambiguous. Also avoid creating competing or conflicting standards for criteria or setting unrealistic goals.
The primary method for success is to prevent challenges before they start. Take ample time with your team at the beginning of the project, follow the steps to identify project success criteria, and hold a thorough team review before the project starts. Once you have a clear set of criteria, create a document and share it with the team.
If you encounter issues with one or more criteria once the project launches, course correct as early as possible. “Create a culture of openness since we all make mistakes,” suggests Quigley. “Make everybody aware that project challenges are learning opportunities, and then move on to improve the situation.”
Remote Teams and Project Success Criteria
Remote teams must operate under the same project success criteria as everyone else. Alignment, communication, and check-ins are fundamental to working with remote and resident teams.
“For every part of the team in my projects, in- and out-of-house, the success criteria are the same,” says Quigley, who manages international teams. “The only thing that might change is the mechanics of keeping this in front of the team members and obtaining the measurements consistently.
Masterfully Track Your Project Success With Smartsheet
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.