What Is Strategic Implementation?
There are numerous definitions of strategic implementation on the web, including the following:
Business Dictionary: The activity performed according to a plan in order to achieve an overall goal. For example, strategic implementation within a business context might involve developing and then executing a new marketing plan to help increase sales of the company's products to consumers.
The Houston Chronicle: The process that puts plans and strategies into action to reach goals. A strategic plan is a written document that lays out the plans of the business to reach goals, but will sit forgotten without strategic implementation. The implementation makes the company’s plans happen.
OnStrategy: The process that turns strategies and plans into actions in order to accomplish strategic objectives and goals.
What these and other definitions have in common is that they discuss turning a theoretical plan (about an organization’s direction) into manageable tasks that team members can perform to achieve the stated goals.
Once an organization creates a strategy, it needs to be implemented, and then executed. Here are the high-level steps in strategic implementation (which we will discuss in detail later):
- Communicate
- Align initiatives with strategy
- Engage staff and outside stakeholders
- Allocate resources
- Make structural adjustments
- Create strategic evaluations
Strategy Implementation vs. Strategic Implementation
Whether or not a difference exists between strategy implementation and strategic implementation depends on who you ask.
In this article, we’ll treat strategy implementation and strategic implementation as synonymous.
Getting Strategic
As organizations evolve, they often change from a reactive to proactive operational style. It’s at this point that an organization begins strategic planning, which leads to strategic implementation.
Formulation, Implementation, and Execution
Strategy formulation (also known as planning), implementation, and execution are intertwined, but each are distinct. Formulation is the creation of a framework that guides decisions. Implementation is preparation and putting elements of the strategy into place. Execution is the decisions made and activities performed throughout the company, with the objective of meeting goals outlined in the strategy.
For example, imagine you're the coach of a football team in a critical 4th-and-1 situation. In this case, the terms would function as follows:
- Formulation: You select a play from your playbook, with the objective of getting a first down.
- Implementation: The players position themselves on the field as outlined in the chosen play, and you place the best offensive linemen up front, and the sturdiest running back in the backfield.
- Execution: The ball is snapped, the linemen push their defensive counterparts back, and if all goes well, they open up enough ground so that when the running back gets the handoff, he can move it across the line of scrimmage for a first down.
Smartsheet offers many templates to assist with strategic formulation.
Thinking About Strategic Implementation
In his paper Strategy Implementation as Substance and Selling, author Donald C. Hambrick and Albert A. Cannella, Jr., state “… implementation must be considered during the formulation process, not later, when it may be too late.” They continue, “The strategist will not be able to nail down every action step when the strategy is first created, nor … should this even be attempted. However, he or she must have the ability to look ahead at the major implementation obstacles and ask, ‘Is this strategy workable?’”
Corporate Strategy and Business Unit Strategy
Executives create the corporate strategy, which determines the company’s lines of business. It also addresses how business units can work together to increase efficiency. Business unit strategy is created by the leader of each unit, and revolves around how the corporate strategy is put into action. In other words, corporate strategy determines what happens, and business unit strategy determines how it happens.
To align corporate and business unit strategies, executives must encourage the development of business unit strategies that both contribute to corporate strategy objectives and respond to their competitive situation, whether geographical or functional.
In a 1984 paper titled Business Unit Strategy, Managerial Characteristics, and Business Unit Effectiveness at Strategy Implementation, authors Anil K. Gupta and V. Govindarajan explain, “The absolute performance of a business entity depends not just on the effectiveness of its internal organization in implementing the chosen strategy, but also on industry characteristics and the choice of strategy itself.”
Top tips to help you save time and money on your next project.
Discover five ways to decrease project delays and increase revenue so you can eliminate the barriers to PMO success and ensure your projects stay on track.
Why Is Implementation Important?
Executives formulate the strategy that business units will execute. However, implementation requires the participation of the entire organization, so implementation is as important — if not more so — than the strategy itself. For example, you can buy seeds and plant them in your garden with the goal of serving a home-grown salad every night at dinner, but that doesn’t ensure that you’ll reach your goal. If you plant at the wrong time of year, if the seeds are not viable in your climate, or if the soil is depleted, you’ll still be buying vegetables from the store for a long time to.
Because strategic implementation is the most important, it’s also the most difficult to achieve. A 1989 Booz Allen study found that 73 percent of managers thought that strategic implementation is more difficult than formulation, 72 percent think that it takes more time, and 82 percent say it’s the part of the process over which they have the least control. But there’s been progress. In a 2015 survey of reports titled Strategy implementation: What is the failure rate?, authors Carlos J.F. Cândido and Sérgio P. Santos conclude that the implementation failure rate has fallen from the between 70-90 percent in the mid 1980s to about 44 percent in the early 2010s.
There are many reasons that strategies can fail. A bad plan (e.g. one that has unrealistic goals), or poor execution (e.g. not adapting to changing conditions) can cause failure, but since implementation is the key aspect, there are more possible pitfalls, including the following:
- Stakeholders Don’t Buy-In: Those who are responsible for executing a strategy won’t want to do it if they don’t believe in it. Ray McKenzie says, “Not having completed buy-in from the team is first and foremost. If people don’t buy-in, it won’t get completed.”
- Resources Aren’t Aligned with Strategy: For example, if you want to sell red balloons, but fill your warehouse with blue ones, you won’t meet your goals.
- Incentives Aren’t Aligned with the Strategy: This happens when you reward people for completing tasks that don’t contribute toward the key performance indicators (KPIs).
- You Don’t Plan to Adjust: Lloyd Baird says, “There’s an old military saying: Your battle plan is great until you contact the enemy, then everything changes. Things are changing so fast in organizations that if you don’t have a method to adapt, evaluate, and change, you’re going to fail. The people that are really good are the ones who are adapting along the way.”
- Continuing To Do Things that Used To Work: Rather than relying on old mechanisms for success, stay current with trends and tools.
- Internal Politics: Turf battles or personal disputes can prevent an organization from properly implementing a strategy.
- Accountability Void: When implementing a strategy, everybody involved must be made aware of their responsibilities, and the consequences of not meeting them.
- No Milestones: As Ray McKenzie explains, “A strategy only works for a period of time — you have to have an outline of those dates.”
- Lack of Empowerment: This happens when people and teams aren’t given the authority, resources, and tools to execute the strategy.
- Communication Breakdown: If the organization is not sharing the strategy, or is sharing it in the wrong ways, the team won’t understand it.
Challenges and Criticisms of Strategic Implementation
Like any business process, strategic implementation has its share of challenges and criticisms. However, if an organization is aware of the limitations of strategic implementation and the obstacles that may arise, they can overcome potential challenges.
Key Leadership Theories for Implementation Strategy
Leadership theories guide how executives think about the world and their organization’s place in it. A couple important, related theories are discussed below.
Tipping Point Theory
- What It Is: The nce a critical mass of people gets behind something, it spreads quickly. Malcolm Gladwell’s 2000 book, The Tipping Point, provides many examples of this theory in action, from the changes in the Bill Bratton-led NYPD in the 1990s that resulted in a dramatic drop in crime, to the way Hush Puppies shoes became popular again once key people in the fashion world started wearing them. The makeup of a critical mass will vary by organization: It could be a majority, or it could be a small group of influential people.
- How It Can Help with Strategic Implementation: While implementing a strategy, executives can identify what constitutes a critical mass in each business unit, and work to get those people invested in the strategy. Once those team members are on board, they’ll bring the rest of the team along.
Blue Ocean Theory
- What It Is: It sprang out of a marketing theory with the same name, which posits that companies should create opportunities in market areas where there isn’t much competition to provide greater growth opportunities. For example, Southwest Airlines became a major player by combining customer-focused service, low prices (partly achieved by flying from secondary airports and partly by using only a single aircraft), and flying to underserved areas. As a leadership theory, Blue Ocean tasks leaders with undertaking the activities that increase team performance, listening to feedback from all parts of their organization, and developing leaders at all levels.
- How It Can Help with Strategic Implementation: Having leaders at many levels focus on activities that increase team performance and listen to every level, the strategies they develop will be easier to implement. This method helps the leaders generate some built-in buy-in. By walking the leadership walk, others are more likely to follow along.
What Do You Mean by Strategic Evaluation?
Strategic evaluation is a type of business performance measurement (BPM) system. In a 2007 paper Towards A Definition of a Business Performance Measurement System, Monica Franco-Santos et al. describes it as, “...a set of metrics used to quantify both the efficiency and effectiveness of actions; or as the reporting process that gives feedback to employees on the outcome of actions.” Strategic evaluation (often written as strategic evaluation and control, when it’s used as part of a strategic management model) is a cyclical process that helps managers and executives determine whether programs, projects, and activities are helping an organization meet their strategy’s goals and objectives. In short, it can help an organization stay on and get back on track.
Strategic evaluation is performed during the execution phase, but you create the process during implementation. There’s always a need to get and analyze feedback to find out what is and isn’t working, identify ways to fix what’s not working, and record the lessons learned for future strategies. There are four high-level steps in the strategic evaluation process:
- Set benchmarks
- Compare results against benchmarks
- Analyze the differences
- Take corrective actions
There are a few different facets of strategic evaluation. Each facet is important and shouldn't be ignored, as using all four ensure that you’ll discover any possible root causes of a problem.
- Premise: Were the strategic goals realistic and achievable?
- Implementation: Was the process of implementing organizational changes based on the strategy performed properly?
- Strategic Surveillance: Are processes and tasks being performed as expected, and if so, are they getting the desired results?
- Special Alerts: While strategic evaluation should take the long view, and not focus too much on short-term fluctuations, it needs to evaluate how changing market conditions and competitors’ actions, as well as unexpected events, affect the strategy. Taking this view will highlight those surprises and changes — then you can implement contingency plans and bring in crisis management teams if required to change the strategy’s execution.
Strategic evaluations are a great way to learn. Ray McKenzie says, “Have a follow-up with the team to see what worked, or if you should do things differently next time around."
How Strategic Implementation Works in Different Organizations
With the rise of mass production in the 19th century, companies began to centralize key functions like sales and finance, which led to economies of scale. Later, as some firms became diversified and began to increase their market, they created business units that focused on product lines or geographical regions. The firms may have lost some of the previously gained economies of scale, but they were able to better react to market conditions.
Centralized organizations could use strategic implementation to make shared services more efficient. Diversified organizations could coordinate processes and goals between various regional offices or product-focused groups.
Later, companies started using the matrix organization to try to take advantage of both the economies of scale created by centralization, and the adaptability of the geographical or product-focused organizations. Matrix organizations are difficult to coordinate. Implementing a strategy can help everyone focus on the same goals.
In the 1990s, the business process reengineering (a version of this is know as Total Quality Management, or TQM) drove the creation of organizations that were organized around processes. Again, implementing a strategy can help everyone focus on the same goals.
Going forward, virtual, networked, and “Velcro” organizations (a concept where the organization can be pulled apart and put back together in response to changes in the business environment, or as Lloyd Baird says, “a network of relationships”) will have the same issues that strong strategic implementation can help.
What Is Involved in the Implementation Process
After formulating and finalizing a strategy, it’s time to share it with the organization. Next, you may need to make changes to the organization in preparation for the execution phase. The steps to take are as follows:
Communicate: Everyone in the organization, and some outside, must learn about the strategy, how it affects them, and what changes they’ll need to make to support it. As you cascade the strategy throughout the organization, different groups will need to be made aware of the parts that are important to them. Sales and marketing teams will want to hear more about the sales goals, while IT will be more concerned about changes to the network and new required software. A vendor will need to know what changes they’ll need make to the materials they provide.
Engage Stakeholders: After communicating the goals, managers and staff (as well as any contractors or vendor affected) need to understand the importance of the strategic goals, their role in strategy execution, their responsibilities, and the impact of meeting or not meeting the goals or fulfilling their responsibilities. Using stakeholders throughout the organization to be champions of the coming changes will make the job easier.
Align Initiatives with Strategy: You’ll likely need to update processes, swap out tools, and make other changes to ensure company activities are contributing to the KPIs laid out in the strategy.
Allocate Resources: What needs to be bought or moved to prepare for execution? What funding needs to be allocated to strategic, operational, and capital expense budgets?
Make Structural Adjustments: Do you need to hire new people? Will there be a round of layoffs? Will you need to change any reporting structures? Are new vendors or contractors required? This is the hardest part of the implementation to perform.
Create a Strategic Evaluation: Implement repeatable processes that will check progress toward the goals, and provide data to executives and managers to determine what changes need to be made to the strategy or it’s execution to keep the organization on track to meeting the goals.
The Three Cs of Strategic Implementation
In a 2012 Forbes article, Scott Edinger composed a concise checklist of considerations. When preparing to implement, keep these in mind:
- Clarify: Avoid high-level statements that only resonate with the C-suite. Write your strategy in a way that connects with front-line employees and managers.
- Communicate: Spread the message in as many ways as you can. Connect the strategy to each group's’ core purpose.
- Cascade: Translate the strategy into actions through the organization. Managers at every level will be the ones who handle this.
5 Changes That Support Successful Implementation
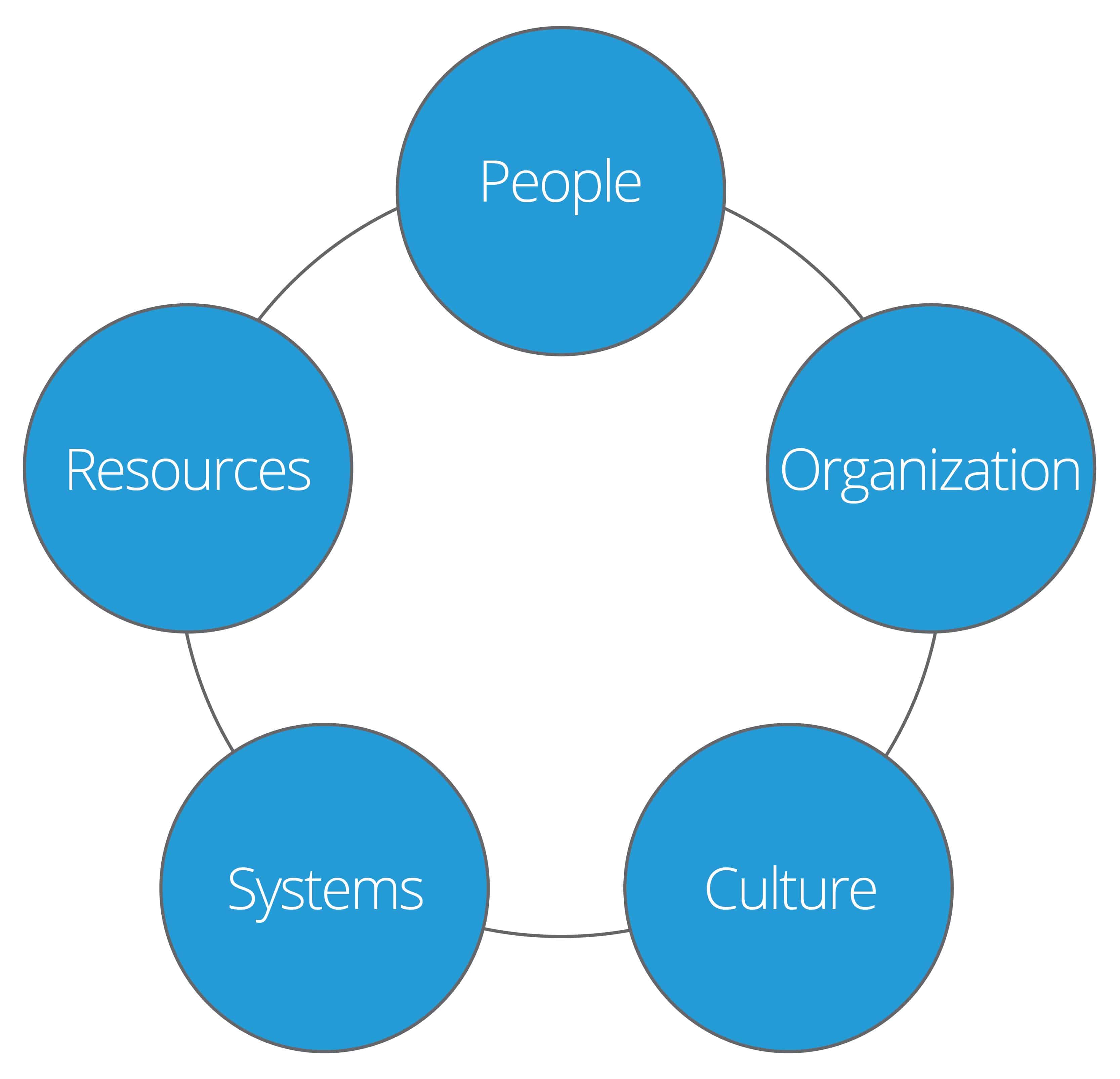
Another lens to look through is, “What changes need to be made to implement the strategy?” You can divide the answer into five groups:
- People: Train or hire the right (and the right number of) individuals to implement plans. Ray Mckenzie advises, “Build a team of people who are key and can help you move your strategy forward.”
- Resources: Get funding and sufficient time to implement required changes.
- Organization: Restructure the company to support the strategic goals.
- Systems: Acquire the tools needed to perform the required processes.
- Culture: Work to create an environment that prioritizes the actions needed to reach the stated goals.
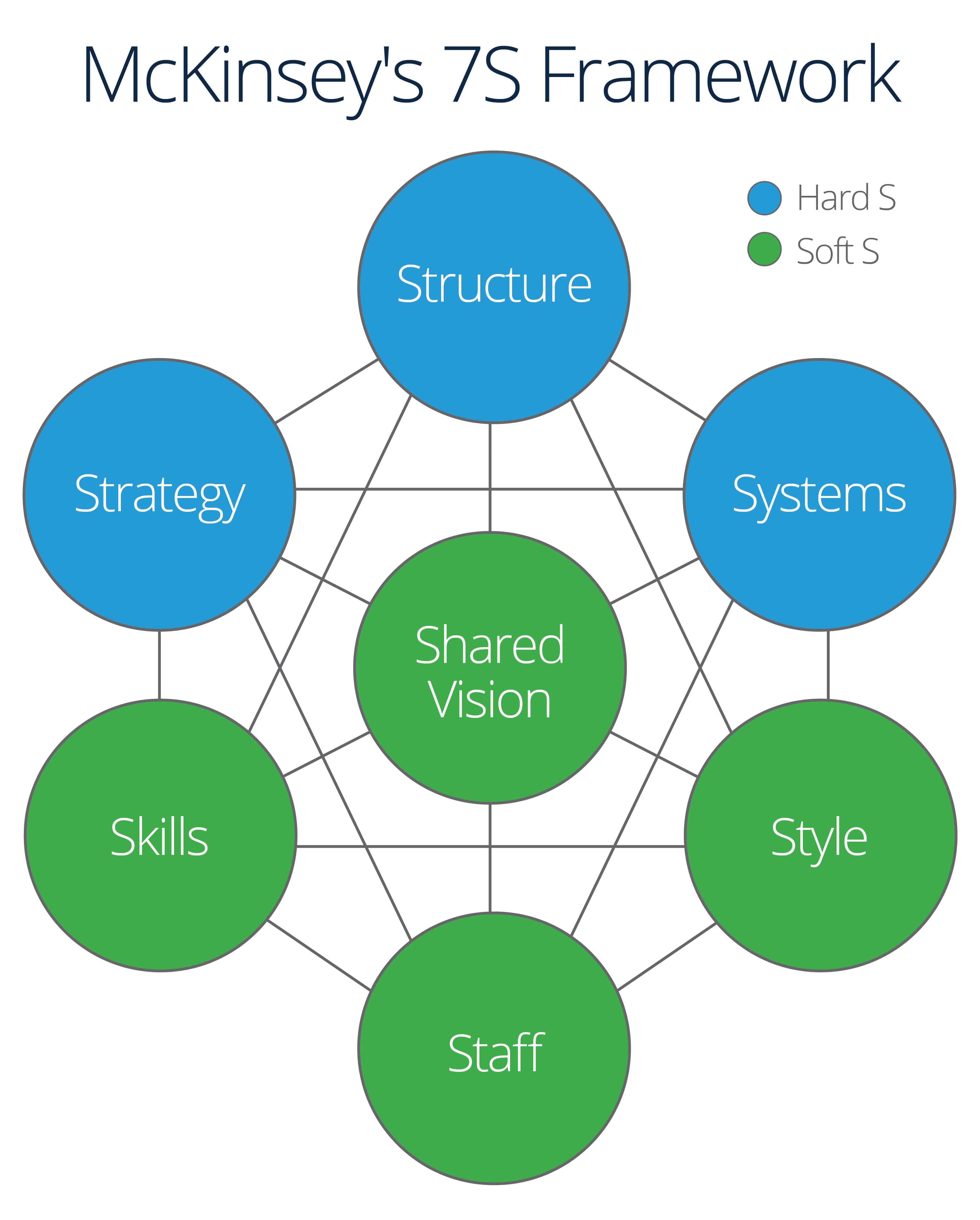
McKinsey 7S Framework
The McKinsey 7S framework is an organizational tool developed at the McKinsey & Company consulting firm in the 1980s, by Robert H. Waterman and Tom Peters. The framework can be used in many ways, including to determine how well an organization is prepared to change in order to implement a strategy.
Here are the 7Ss:
- Strategy: What needs to to be implemented
- Structure: The chain of command
- Systems: The tools used to perform tasks and complete processes
- Skills: What employees can do
- Style: How the leaders lead
- Staff: The employees
- Shared Values: The core values, expressed through the corporate culture
These can be divided into the hard Ss (Strategy, Structure, Systems), which are tangible, and the soft Ss (Skills, Style, Staff, Shared Values), which are intangible. In order to ensure smooth implementation, align each of these categories.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Implementation Strategies
As previously mentioned, because strategy formulation, implementation, and execution are intertwined, it may difficult to know which phase is the cause of strategic failure. Here are some quick examples of success and failure where implementation is key.
Wal-Mart: The corporation became the retail giant they are by having low prices. They made lower margins by having high volume. In order to do that, they implemented a supply chain strategy that reduced operating costs. As they grew, their strategy was to use their size as a bargaining chip with suppliers to get even lower prices.
J.C. Penney: Penney’s was a major retailer in the U.S. for many years, but when the landscape changed, they kept doing the same things. When the company finally brought in new leadership in 2011, they implemented a strategy that eliminated coupons that customers used and lowered their regular prices. They also changed their retail mix. When sales began to fall, they maintained their implemented strategy without adjusting. If they had taken advantage of the data from strategic evaluations and had responded appropriately, they might have been able to salvage the parts of their strategy that were working.
Apple: In the late 1990s, Apple was close to going out of business. They had many products that didn’t sell. When Steve Jobs returned, he implemented a strategy that reduced the number of products, and worked to develop new ones. This approach eventually led to the invention of the iPod. The iPod was not the first MP3 player, but it was the first to catch on because of its ease of use and storage capacity. This, in essence, was an application of the Blue Ocean theory: Apple found a market segment that wasn’t very competitive, and created a product that was better than what was available. For a long time, Apple was the dominant player in that market segment.
Google: While Google is successful in most ventures (search, email, maps), they have had some notable stumbles. One is Google Glass, the company’s wearable computer. While the idea was good, the device was very expensive, was not easy to use, there were concerns about privacy, and was an unattractive pair of glasses. Mostly, there was no real compelling reason to use it. Google Glass was a failed application of the Blue Ocean theory, and also another failure to adapt to data from strategic evaluations.
Strategic Implementation without Disruption
Strategic implementation can involve the restructuring of reporting relationships: adding, deleting, or updating processes, or even layoffs. This process can be painful for employees, and can cause problems when it’s time to execute strategy.
Restructuring can be expensive, and the new structure can create issues as troublesome as those you are trying to solve. Employes have to adapt to the new structure and may be dissatisfied. As a result, a lot of tacit institutional knowledge can be lost as people get shuffled around or worse, leave the company. Restructuring may also result in maintaining legacy systems until they can be phased out, which causes unnecessary expense. Additionally, some people won't be able to fully focus on the new strategy while they keep legacy systems running.
It's far less disruptive to choose an organizational design that’s flexible and can be adapted without major conflicts, and then formulate strategies that can be easily implemented.
Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton recommend the balanced scorecard framework, which they co-created in the 1990s. They believe that this framework will minimize the need to go through disruptive restructuring when new strategies change due to the following reasons:
- It focuses on the strategic agenda of the organization.
- It recommends monitoring a small number of data points.
- It looks at both financial and non-financial data.
The implementation of this framework is beyond the scope of this article, but you can read an explanation of its benefits via the Harvard Business Review.
Sometimes disruptive restructuring is necessary. If it can’t be avoided, here are some steps to make it more manageable:
- Break the strategy into smaller chunks, so the disruption is spread over a longer time frame.
- Communicate directly to affected employees. Explain why the changes are needed, and retrain them to adapt to the new structure.
- Use a version of the strategic evaluation process that focuses on the affected employees, have them report their on satisfaction levels, and adjust the strategy based on that feedback to lessen the impacts.
Improve Strategic Implementation with Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.