What Is Production Scheduling?
Production scheduling is the process of determining when products will be manufactured to maximize efficiency while limiting stockouts and unbalanced inputs and outputs. This process includes optimizing where, when, how, and what materials you will use to manufacture your products.
A successful production schedule will help you do the following:
- Plan for changing supply and demand
- Organize workers and contingency plans
- Maintain stock, even with delays
- Refine efficiency and note areas of possible improvement
- Standardize communication across a company
- Determine costs for parts and labor
- Identify opportunities for improvement
- Eliminate disruptions to workflow
- Establish relationships with vendors and other third parties
- Improve visibility across all company platforms
These schedules are flexible documents, and may include different variables relevant to the current production period. A successful production schedule will also report on critical supply chain key performance indicators (KPIs), including the following:
- Performance, daily or otherwise
- Reductions in cost
- Service rates
- Production times
- Cycle times
- Order management
Production Scheduling vs. Production Planning
While a production schedule is determined by short-term factors, production planning takes a longer time frame into consideration. Production plans are determined by the ideal times to produce products for on-time deliveries, capacity plans, and material requirements.
Production schedules are relatively flexible and adapt to changes in manufacturing operations, but production plans are required to stick to predetermined timelines. Production planning also considers the following:
- Timeframes
- Type and amount of necessary product
- Raw materials
- Required workstations
The Importance of Production Scheduling
Production scheduling is a crucial part of the manufacturing process that helps to ensure efficient production times, decrease costs and product shortages, and eliminate interruptions, delays, and waste.
Production scheduling also concerns the following eight elements:
- Parts Distribution: Production schedules reduce bottlenecks and downtime by distributing the correct type and number of parts to workers throughout the production timeline.
- Stock Levels: Scheduling helps guarantee that you maintain stock levels, keep warehouses organized, and can account for all outputs.
- Labor Distribution: A production schedule can help you record and maintain working hours, overtime, and the number of workers needed during a shift or production period.
- Equipment Performance: Equipment analysis and scheduling allow manufacturers to optimize workstations and equipment usage, which reduces the need to purchase extra or overuse equipment.
- Finance Optimization: Schedules help companies allocate resources efficiently and optimally, which decreases financial emergencies and increases the reliability of available funds.
- Product Quality: Optimally planned production schedules can increase the quality of products across a shorter time frame.
- Customer Relationships: Production schedules help keep customer orders fulfilled on time, and can help increase satisfaction, trust, and brand loyalty.
- Company Reputation: Companies that optimize manufacturing schedules are known for being timely, economical, and considerate of both their workers and customers.
Production templates can help you keep these priorities in mind while creating a top-notch schedule personalized for your organization.
Six Production Scheduling Steps
Creating a production schedule requires you to balance customer needs with your organization’s available time and resources. Whether you’re creating a product or producing a video, your production schedule should consider or include steps for planning, routing, scheduling, dispatching, executing, and maintaining.
These six steps are outlined in more detail below.
1. Planning
During the first step, a company will analyze resources, budgets, staff, stock, and timelines to evaluate the status of the production processes. There are two types of planning methodologies:
- Static Planning: This type of planning assumes nothing will change during the production process.
- Dynamic Planning: This type of planning assumes anything could change during the production process.
At this stage, you should also set strategic goals and calculate labor and capacity.
2. Routing
In the routing step, a company will determine the path that raw materials must take from their original form to a finished product. This also includes determining the most efficient, cost-effective steps in the manufacturing processes.
3. Scheduling
This step is used to officially determine the dates and times for a project using a company’s specific methodology. You can create different types of schedules, including the following:
- Master Schedules: Full-scale, summary-level schedules that include breakdowns for labor, routing, resources, and more.
- Manufacturing Schedules: These are more limited schedules that only include the routing steps.
- Retail Operations Schedules: These are retail-focused schedules that include routing steps for retail and e-commerce products.
4. Dispatching
Dispatching refers to issuing orders concerning the locations of people, parts, and products. In this step, a company determines how these items will reach their designated locations during the entire scheduling process.
5. Executing
This is when the company actually carries out the production schedule from beginning to end — and thus, sinks or swims. If researched and created effectively, the schedule should create a smooth production process.
6. Maintaining
After a company executes the production schedule, two-way communication between management and workers begins. This step can help a company determine areas for improvement, which it can then take action on.
How to Optimize Production Scheduling
Since there are different methodologies, contributors, and factors that either change or depend on an up-to-date production schedule, it’s crucial to continually optimize. One of the best ways to do this is to incorporate agile planning into your scheduling process.
To do this, consider the following:
- Dynamic Scheduling: Prepare for changes in distribution, resource allocation, labor usage, worker capacity, and more by developing an adaptable schedule.
- Work-in-Progress Control: Determine a priority schedule and label projects by importance to keep urgent and significant projects on track.
- Prioritized On-Time Deliveries: Determine priority based on need and resources, rather than on the due date.
- Inventory and Supply Management: Coordinate resource arrivals and availability to ensure projects can continue on schedule with minimal product loss or confusion.
- Maintained Equipment and Facility: Working equipment and machinery allow workers to produce products on time, while also keeping laborers safe and protected.
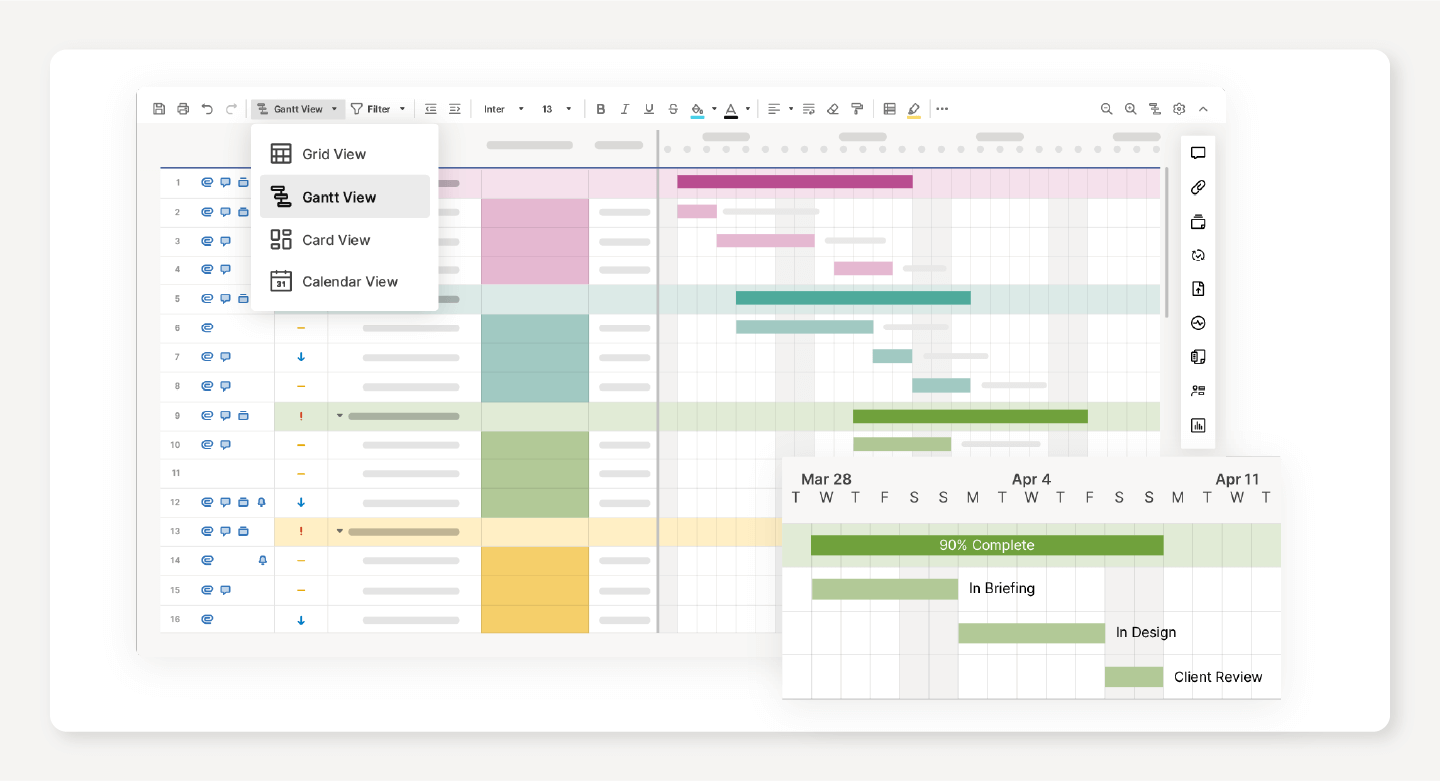
- Production Scheduling Software: You can also use project scheduling software to efficiently and effectively manage orders, track inventory, organize laborers, and more.
What Is Production Scheduling Software?
Production scheduling software allows you to determine, build, and manage your production schedule from one platform. This type of software — also known as Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software — allows you to create dynamic, up-to-date schedules across diverse teams.
Many companies use simplified tools for scaled-down operations schedules. However, there are some downsides, as tools like Excel and Google Sheets can:
- Create bulky files
- Lack integration and functionality options
- Increase human error possibilities
For companies with larger-scale scheduling or enterprise resource planning needs, production scheduling software can be an incredibly powerful tool with a variety of benefits and capabilities.
If you’re considering a software program, evaluate your options by examining the following:
- Integration possibilities with current enterprise resource planning (ERP) and manufacturing resource planning (MRP) software
- Central database capabilities
- Possible data formations
- User and worker access
- Available tools, including calendars, charts, and item tracking
Benefits of Production Scheduling Software
Production scheduling software can be expensive, and new programs can take time and resources to implement. However, the following seven benefits often outweigh the costs and setup times:
- Increased utilization of resources, workstations, and laborers
- Reduced inventory waste
- Prioritized on-time deliveries
- Synchronized manufacturing processes
- Visibility of projects across all teams
- Improved project management capabilities
- Better customer service and satisfaction
Optimize Production Scheduling With Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.