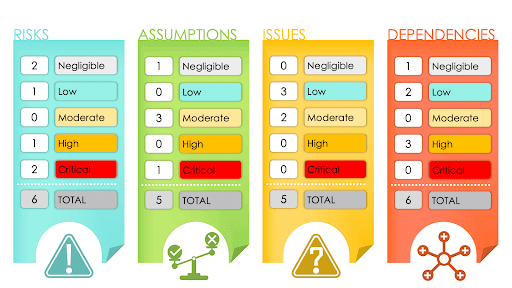
What Is a RAID Log?
A RAID log is a project management tool used for tracking project risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies. In recent years, the A and the D in RAID have also been used to refer to actions and decisions, respectively. This tool makes it easier for project managers to gather and understand information, ensuring that projects finish on time and within budget.
These are the key elements of a RAID log:
- Risks: These are potential events or vulnerabilities that might negatively impact a project.
- Assumptions/Actions: Assumptions are factors that are assumed to be true for a project to be successful. Actions would mean that you use this column to list all the action items from meetings and is best used for a project with lots of moving parts.
- Issues: These are current problems that negatively affect a project and require resolution.
- Dependencies/Decisions: Dependencies are tasks, processes, or deliverables that a project relies on to meet its objectives. A RAID log that uses decisions would document any decisions made during a project in this column. Using decisions is a good choice when you need to document all the choices made in this project for use in future ones.
Caption: This RAID log image depicts the long-standing use of RAID instead of the newer version that can swap out assumptions for actions and dependencies for decisions.
Typically the project manager creates the RAID log and shares it with the project team and other relevant stakeholders. Managers might also loop in project sponsors, higher-level management, and other individuals or groups with a vested interest in the project.
Learn more about incorporating RAID logs into your project management with this guide to RAID project management.
What Should You Include in a RAID Log?
A RAID log should include detailed information about the risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies of a project. It should also note the impact and probability of each item and might include the status and resolution plan for issues.
Here are the elements you can include in a RAID log:
- RAID Category: Identify whether the item is a risk, assumption, issue, or dependency.
- Description: Provide a brief explanation of the item, clearly stating each risk, assumption, issue, or dependency.
- Impact: Summarize the potential or actual impact of the item on the project. The impact might include potential delays, additional costs, or other adverse effects.
- Owner: Specify the person or role responsible for managing or resolving the item.
- Priority: Indicate the urgency or importance of the item. The categories of importance are critical, high, moderate, or low. Teams should address critical and high-priority items immediately and schedule time to address medium- or low-priority items at a later date.
- Status: Denote the current status of the item.
- Action Plan: Outline the steps needed to manage or resolve the item. This section should provide a clear path for addressing the item and might include deadlines for completion.
- Due Date: Indicate the expected date by which the item should be resolved.
Here’s an important tip: Remember to label each section clearly and return to your document regularly to make sure its information is correct and up to date.
RAID Log Examples and Samples
Reviewing sample RAID logs can help you craft your own, as they demonstrate the practical application of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies in real-world contexts. By studying these examples, you can learn how to categorize and detail each component.
Here is an example of a RAID log for a building construction project:
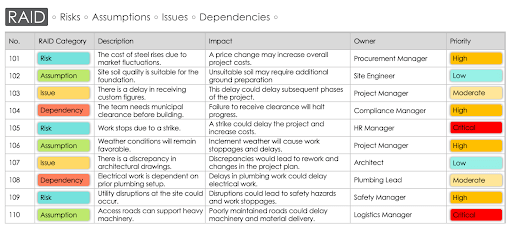
Here is another example of a RAID overview, which lists the general risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies for a sample IT project:
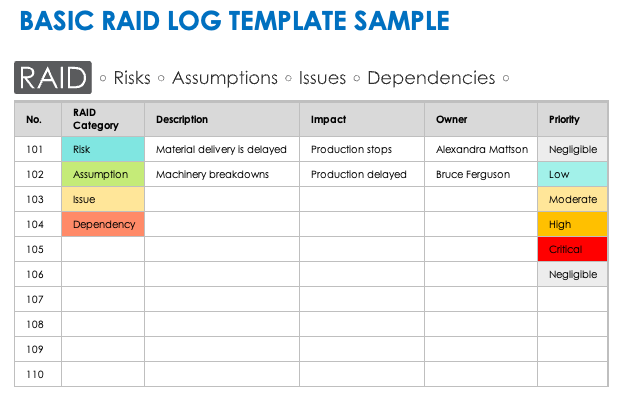
Basic RAID Log Template With Sample Data
Download a Sample Basic RAID Log Template for
Excel
|
PowerPoint
| Google Slides | Google Sheets
Download a Blank Basic RAID Log Template for
Excel
|
PowerPoint
| Google Slides | Google Sheets
Create your own RAID log with this basic, editable RAID log template. For every task, feature, or event in your project, choose the suitable RAID category, provide a description, highlight its impact on the project, allocate a team member to take responsibility, and assign a priority level. There are two versions of this template available for download: a blank version and one with example text to help you navigate through the RAID log procedure.
For even more RAID log templates, including RAID analysis matrix logs, see this collection of free RAID templates.
When to Use RAID Logs
Use RAID logs at the commencement and throughout the duration of a project. When you update the RAID log regularly, you’ll receive timely responses to emerging challenges, allowing you to adjust, keep your project on track, and achieve its objectives.
The earlier that a project manager incorporates a RAID log into their project planning, the better prepared they are to navigate obstacles and ensure the project stays on track.
“In my experience, RAID logs should be initiated at the outset of a project,” says Teresha Aird, Co-Founder and CMO at Offices.net. “They're integral to mapping out potential challenges and dependencies during the early stages.”
RAID logs come in handy in every phase of the project lifecycle. Refer to the following graphic to see how RAID logs come into play at different project milestones:
Who Uses RAID Logs?
RAID logs are a versatile tool that stakeholders in different positions and industries use to ensure that projects are completed successfully, on time, and within budget. Everyone from business analysts and risk managers to supervisors and managers uses RAID logs.
Below are some of the key individuals who use RAID logs:
- Business Analysts: RAID logs help analysts understand business requirements, assess potential risks, and identify issues and dependencies that need addressing.
- Risk Managers: RAID logs help risk managers identify, assess, and prioritize risks, a process that allows them to develop effective risk mitigation strategies.
- Team Leaders and Supervisors: RAID logs help leaders keep track of their team's tasks, identify potential issues, and ensure that their projects are progressing smoothly.
- Project Managers: RAID logs help managers maintain oversight of factors that could impact a project.
“A RAID log is a valuable tool in project management,” says Percy Grunwald, a personal finance expert and Co-Founder of Compare Banks. “It should be utilized when managing complex projects involving multiple variables that could impact a project's success. RAID logs help project managers proactively identify and address potential risks, challenges, assumptions, and dependencies, ensuring that projects stay on track and potential issues are mitigated.”
These industries commonly use RAID logs:
- Information Technology: IT projects often involve complex systems and software development, making RAID logs an essential tool for managing various project elements.
- Construction: In construction, RAID logs help teams identify potential risks and issues related to a project, such as delays due to weather, dependency on suppliers, and more.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, project managers use RAID logs to manage healthcare system improvements, the implementation of new systems, and other key initiatives.
- Manufacturing: Leaders in manufacturing use RAID logs to identify and record potential issues and dependencies related to production, the supply chain, and logistics.
- Consulting: Consultants use RAID logs to assess the risks and issues in client projects and recommend strategies to manage those concerns effectively.
What Are the Benefits of Using a RAID Log?
A RAID log is a centralized, organized tool that enables more effective project management and timely decision-making. It enhances communication, transparency, and accountability with the project team, helping to mitigate risks, address issues, validate assumptions, and manage dependencies proactively.
These are some of the key benefits of utilizing RAID logs:
- Better Decision-Making: A RAID log offers insights that enable teams to make more informed, timely, and effective decisions throughout the project lifecycle. “By identifying risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies upfront, project teams can make informed decisions and take necessary actions to prevent or mitigate potential roadblocks,” says Grunwald.
- Increased Accountability: The use of a RAID log ensures that team members are aware of their responsibilities, their roles, and the risks or issues they are tasked with managing.
- Improved Communication: A RAID log enhances transparency and facilitates better communication among project team members and stakeholders. “This proactive approach enhances project efficiency, reduces surprises, and ultimately contributes to better project outcomes,” explains Grunwald.
- Enhanced Time Management: By assisting in the timely identification and resolution of issues, a RAID log ensures that a project stays on schedule.
- Preserved Audit Trail: Maintaining a RAID log preserves a detailed record of all risks, issues, assumptions, and dependencies, offering valuable insights and references for future projects or audits. “RAID logs provide a structured framework for capturing and organizing key project elements, allowing for easy tracking and monitoring,” says Grunwald.
- Enhanced Actionability: A RAID log provides a structured and detailed overview of all project-related elements, making it easier to take timely, informed, and effective actions. “It functions as a roadmap, guiding teams toward what needs attention and action,” says Aird.
- Amplified Clarity: By clearly outlining and organizing project risks, issues, assumptions, and dependencies, a RAID log reduces ambiguity and enhances overall project focus, coordination, and clarity. “RAID logs provide a structured overview of all significant aspects of a project,” explains Aird. “Over the years, I've observed that our most successful business tenants employ RAID logs to ensure comprehensive project oversight.”
What Are the Challenges of Using a RAID Log?
A RAID log comes with many benefits, but requires meticulous and consistent updates that can be time-consuming and might require additional resources. A RAID log also needs to be accessible and understandable to all relevant stakeholders, which can be difficult.
“While a RAID log offers numerous advantages, it can also present challenges,” says Grunwald. “One potential issue is that of overlooking or underestimating certain risks or dependencies. Additionally, maintaining and updating a RAID log requires ongoing effort and communication. Ensuring that all team members contribute to and stay engaged with a RAID log can be a challenge, particularly in large or distributed teams.”
Here are some common challenges associated with RAID logs and how to address them:
| Challenge | Why It’s a Problem | How to Fix It |
|---|---|---|
| Data Overload | A RAID log can become overwhelming if it is overloaded with excessive information. | Prioritize information and regularly review and update your log to ensure that it remains focused on essential data. |
| Decision Paralysis | The information in a RAID log can lead to decision paralysis. | Use the log as a tool for informed decision-making, not as the sole basis for decisions. |
| Information Silos | Information in a RAID log might become siloed, limiting its visibility and utility. | Ensure that the log is easily accessible to all team members, and encourage regular communication and updates. |
| Risk of Overlooking Critical Elements | You can potentially overlook or underestimate certain risks or dependencies in a RAID log. | Review and update the log regularly, ensuring diverse team input for a comprehensive view. |
| Skill Gap | A lack of experience or expertise in maintaining a RAID log can lead to ineffective use. | Provide training and resources to the team members responsible for maintaining the RAID log. |
| Stakeholder Resistance | Stakeholders might resist the use of a RAID log, doubting its effectiveness. | Clearly articulate the benefits of the log, and demonstrate its impact on project success. |
| Tool Limitations | The limitations of the tools used for RAID logging can restrict the ease of updating and accessing a log. | Choose a robust and flexible tool that is easily accessible to all team members. |
RAID Log Best Practices and Expert Tips
When implementing RAID logs, you must update information regularly and precisely to keep current. You must also maintain clear and open communication channels, so all stakeholders can stay informed, encouraging collective responsibility and proactive problem solving.
Here are some best practices and expert tips to keep in mind as you start to use RAID logs:
- Assign Ownership: By clearly assigning ownership for each element in the RAID log, teams can ensure accountability, promoting efficient problem solving. “Designate an individual or a small team to manage the RAID log,” advises Aird. “Doing this ensures accountability and currency.”
- Keep It Simple: Maintaining simplicity in the RAID log encourages regular communication among and contribution from all team members. “While it's essential to be thorough, it's equally crucial to be concise,” explains Aird. “A RAID log should be easily comprehensible to anyone who reviews it.”
- Maintain a Routine: By establishing a regular habit of updating and consulting the RAID log, you can ensure that no element is overlooked. “Maintain a routine for updating the RAID log, ideally during project status meetings, to ensure that it remains current and relevant,” suggests Grunwald.
- Maintain Open Communication: When used correctly, a RAID log can enhance project transparency and communication. “Encourage open communication among team members to ensure that all inputs are captured accurately,” says Grunwald.
- Prioritize Entries: By prioritizing entries in the RAID log, teams can better allocate resources strategically, reducing potential project delays and obstacles. “Prioritize entries based on their potential impact on the project's success and allocate resources accordingly,” suggests Grunwald.
- Schedule Regular Reviews: Scheduling regular reviews of the RAID log ensures continual project assessment, allowing for timely adjustments and interventions. “Schedule regular reviews of the RAID log to reassess and adjust strategies as needed,” recommends Grunwald.
Effective vs. Ineffective RAID Log
An ineffective RAID log tends to be maintained sporadically, cluttered, and lacking clear ownership assignments. In contrast, an effective RAID log and its items are updated regularly, organized clearly, and assigned accurately, serving as a reliable resource for managing projects.
In the following example, there are several key issues that make this RAID log an ineffective tool.
Here are some of the problems with this RAID log:
- Descriptions Are Vague: It is unclear what each item entails, making it impossible to address an issue properly.
- Details Are Missing: There is a lack of complete information in various fields.
- Due Date Is Ambiguous: Terms like "soon" and "later" do not provide clear timelines.
- Impact Is Not Clearly Articulated: Terms like "bad" and "not good" do not give insight into the potential effects on the project.
- Owner Is Unclear or Missing: Without a designated owner, no one is accountable for managing the item.
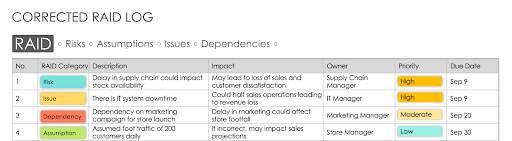
There are several ways to correct the RAID log above. Review the following log to see how it is more specific and helpful.
These are some key differences to note:
- Clear and Specific Descriptions: Each item is described clearly, providing insight into the nature of the risk, issue, dependency, or assumption.
- Color-Coded Categories: Although it’s not a requirement, color-coding factors such as priority levels or statuses can help users prioritize information more easily.
- Complete Information: All fields are filled out with detailed and relevant information.
- Designated Owners: Each item has a designated owner responsible for its management.
- Specific Due Dates: Each item has a clear and specific due date.
- Well-Articulated Impact: The impact is clearly defined, allowing for a thorough understanding of the potential effects on the project.
RAID Log vs. Issue Log
While issue logs exclusively track and manage problems that have already arisen in a project, RAID logs provide a more comprehensive view by also monitoring risks, assumptions, and dependencies, helping in both proactive and reactive project management.
Teams can effectively employ both RAID logs and issue logs to ensure comprehensive project management. Use both logs in complex, high-risk projects or projects with numerous dependencies and assumptions, allowing for detailed issue tracking alongside proactive risk and dependency management.
For issue logging resources, see this all-inclusive list of free issue tracking templates.
RAID Log vs. Risk Register
While a RAID log is a management tool that provides a comprehensive overview of multiple factors, a risk register focuses specifically on identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks, allowing for a concentrated and detailed approach to risk mitigation.
For a comprehensive list of downloadable risk registers, see this collection of risk register templates.
For a complete analysis comparing and contrasting RAID logs, issue logs, and risk registers, refer to the following chart:
Feature | RAID Log | Issue Log | Risk Register |
|---|---|---|---|
Complexity | Is generally more complex due to broader scope | Is simpler, as it focuses only on issues | Complexity can vary, but generally focuses on risk assessment and mitigation strategies |
Ownership Assignment | Assigns ownership for risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies | Assigns ownership for issues | Assigns ownership for risks and related mitigation strategies |
Proactivity | Helps in proactive management by including risks and assumptions | Is mainly reactive, dealing with existing issues | Aims at proactively identifying and managing potential risks before they become issues |
Purpose | Aims to manage and mitigate potential and actual project challenges | Aims to track and resolve issues within project’s scope | Aims to identify, assess, and prioritize risks to minimize their project impact |
Scope | Covers risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies | Focuses primarily on tracking issues | Focuses exclusively on identifying and tracking risks |
Use of Resources | Might require more resources for management and review | Typically requires fewer resources | Might require dedicated resources for risk analysis and management |
Take a look at this collection of risk assessment matrix templates or these free risk management templates for more risk management resources.
Do You Use a RAID Log in Agile?
You can use a RAID log in Agile project management. Even though Agile emphasizes adaptability and iterative progress, using a RAID log in Agile projects provides a structured approach to managing project elements while still aligning with Agile’s adaptive principles.
Here are some ways to incorporate RAID logs into your Agile projects:
- Sprint Planning: Use RAID logs in sprint planning to systematically identify and document potential risks and dependencies for the upcoming sprint. Find tips and tools in this sprint planning article.
- Stand-Ups: In stand-ups, use RAID logs to craft concise updates on new issues and dependencies that might be obstructing progress.
- Retrospectives: Employ RAID logs in retrospectives to analyze and adjust the tracked items, helping the team to learn from past sprints. Learn how to run a retrospective meeting.
- Product Backlog Refinement: Apply RAID logs in product backlog refinement to continuously assess and update risks and dependencies related to backlog items.
- Stakeholder Check-Ins: Refer to RAID logs during stakeholder check-ins to clearly communicate high-impact risks and issues.
- Release Planning: Incorporate RAID logs in release planning to highlight and account for dependencies and risks that could impact the release timeline.
- Agile Scaling: When scaling Agile across multiple teams, use a RAID log to maintain a global view of risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
- Continuous Improvement: Use RAID logs to align with Agile’s commitment to continuous improvement by regularly updating and reviewing the log, ensuring it contributes to the project’s evolving needs.
In summary, a RAID log is an effective tool in any form of project management, especially when teams use Agile methodology.
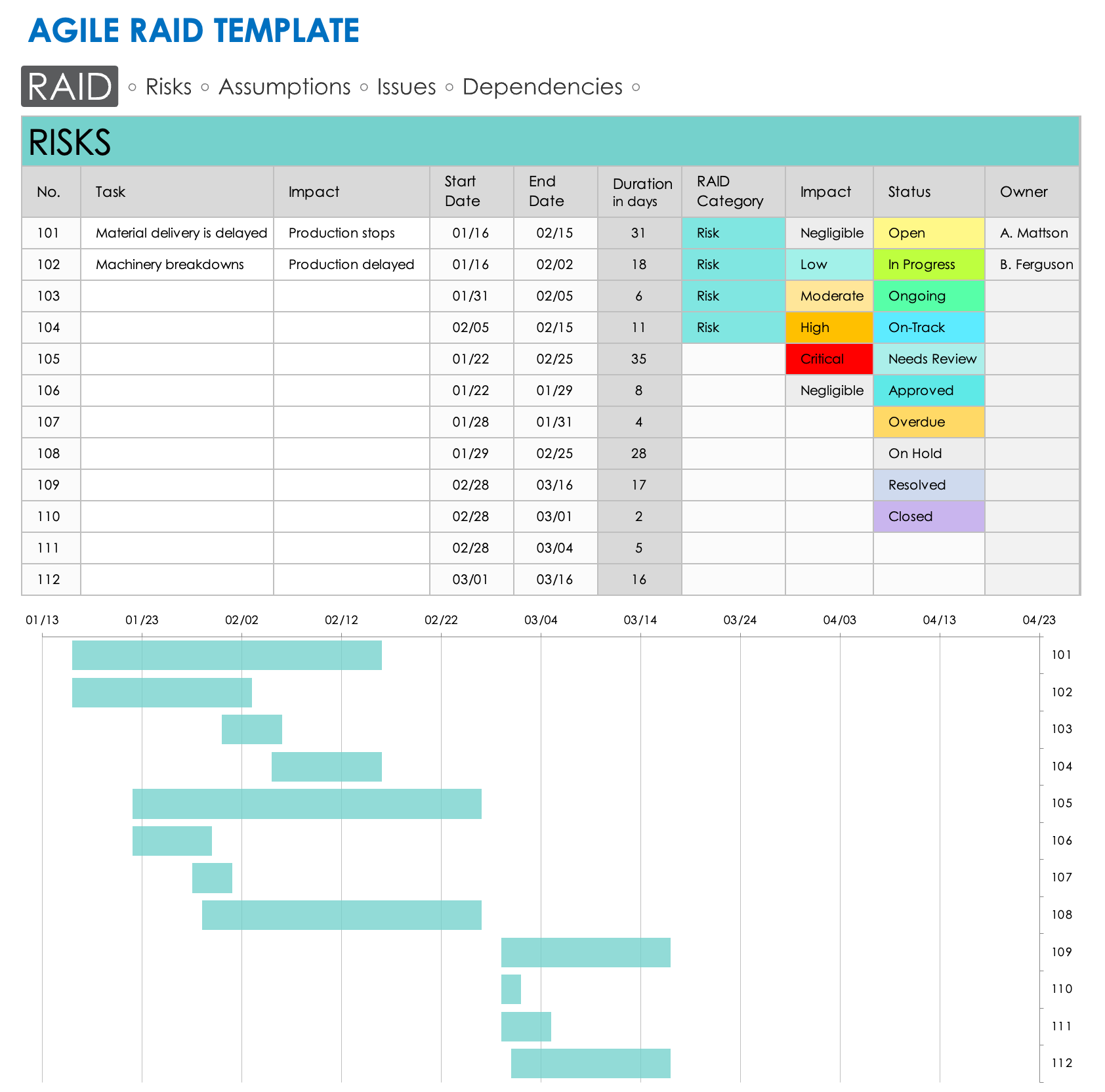
Agile RAID Template
Download an Agile RAID Template for
Excel
| Google Sheets
Agile teams need an adaptable method to note potential risks and revisit assumptions during a project. This Agile RAID template enables teams to do just that. Simply enter your identified risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies in the appropriate worksheet, along with their impact, start and end dates, status, and owner. The template will generate a timeline chart at the bottom of each worksheet, so you can track your RAID elements over time.
For more resources and information about Agile methodology, see this all-inclusive guide to Agile project management.
How to Implement a RAID Log
To implement a RAID log, start by assembling a project team and designing the project scope. Prioritize regular updates, comprehensive reviews, and continuous communication with stakeholders, and use the log insights to make strategic adjustments.
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating and implementing a RAID log:
- Assemble Project Team: Gather a dedicated team with diverse skills to oversee the RAID log.
- Identify Project Scope: Clearly define and detail the project boundaries and goals. Maintaining this focused direction mitigates the risk of future misunderstandings and scope creep.
- Conduct Initial RAID Session: Organize a collaborative session to identify project risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
- Categorize, Prioritize, and Assign Items: Organize and allocate RAID items systematically by using consistent ranking and assignment methods.
- Establish and Communicate Timelines: Define clear timelines and milestones, and employ visual tools for effective tracking and communication, keeping the project and team members on schedule.
- Choose Effective Tools: Select a project management template, software, or other organizational tool that suits your project’s needs. User-friendly project management software can be a great option for efficient RAID log maintenance and seamless team integration.
- Update and Review Log Regularly: Update the RAID log regularly in scheduled team meetings.
- Ensure Compliance and Adjustment: Audit the RAID log regularly for compliance, and adjust project plans proactively based on RAID insights.
- Communicate With Stakeholders: Maintain open communication, sharing RAID log updates with stakeholders and encouraging their continuous input for informed and collaborative decision-making.
- Close and Learn From the Project: At project closure, confirm the final status of each RAID item and use the completed RAID log for post-project evaluation. By doing so, team leaders can foster a culture of ongoing improvement.
What Is a RAID Log in Smartsheet?
Master Project Management with RAID Logs and Analysis from Smartsheet
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.