Elements of a Go-to-Market Process
The process of bringing a new product to market begins with researching the market landscape, understanding the target consumer, and deciding on appropriate distribution channels. These elements will shape a comprehensive GTM strategy for sales and marketing teams to implement.
Here are the crucial elements of the GTM process:
- New Product or Service: First, you must have a product that is ready to launch and aligns with market needs. You can use a product launch roadmap template to visualize the final stages of product development leading up to the launch. This includes testing the user experience, which provides valuable insights into how the product addresses customer pain points.
- Market Research: Data from the market landscape provides crucial information on how to successfully launch a new product. Companies should research their competitors’ successful promotional and sales tactics, as well as compile demographic and psychographic data to understand their target audience.
- Product-Led or Sales-Led GTM Strategy: The GTM process might differ depending on which GTM strategy best aligns with your product, customer behavior, and business resources. A product-led GTM strategy means that sales take place within the product itself, generated through free trials or other freemium models that highlight its unique features. A sales-led GTM strategy employs traditional sales tactics, including lead-nurturing, demos, and direct connections between prospects and the sales team.
- Marketing Strategy: To promote the product or service effectively, companies need to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy that includes a compelling value proposition and communication plan. Choose marketing channels (social media, email, advertising, etc.) that will best reach the target audience — this is a key element of any successful marketing strategy.
- Sales Strategy: The right sales model depends on the product, the typical buyer’s journey, and the company’s resources. For example, a self-service model that relies on marketing to drive customers to the product works best in a business-to-customer (B2C) context with online sales. In contrast, an inside sales model involves a longer cycle of lead-nurturing that suits more complex or business-to-business (B2B) products. Learn more about how to build a sales process and other possible sales methodologies to employ.
- Product Launch: A successful product launch requires careful coordination and execution across multiple teams. This phase involves setting clear launch goals, coordinating marketing and sales efforts, and ensuring that you handle all logistical aspects, from supply chain readiness to customer support systems.
- Metrics and Optimization: The GTM process doesn’t end at product launch. Instead, define and track success metrics that align with business goals, evaluate results, and adapt to changes in the market or updates to the product. Common metrics include conversion rates, customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer satisfaction scores, and return on investment (ROI).
GTM Strategy Frameworks
A GTM strategy framework is a structure you can use to develop a comprehensive marketing and sales plan. These frameworks are similar to classic marketing processes, but are adapted for the GTM context.
Learn more in this guide to strategic marketing processes and planning.
Here are four potential GTM strategy frameworks:
- Four Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion): The foundation of a classic marketing mix, the 4Ps inform many aspects of strategic marketing, including GTM strategies. This framework prompts you to consider the essential steps in a GTM process: the features that set your product apart, a competitive pricing strategy, a distribution plan, and how you’ll market to your audience. The 4Ps offer a great starting point for product-led GTM strategies that rely on unique features and marketing to drive sales.
- Seven Ps (Four Ps plus People, Process, Physical Evidence): Expanding on the 4Ps, the 7Ps include additional details, such as which team members are responsible for each element of the strategy and customer-facing communication, the operations that ensure a smooth distribution, and packaging and branding. This framework is useful for service-oriented businesses or sectors where customer interaction, the service delivery process, and physical or digital interaction points are critical.
- Five Cs (Company, Customers, Competitors, Collaborators, Climate): This framework prompts you to consider both internal and external factors that might impact your product’s market entry. It focuses on the company’s goals and brand identity, target audience, competitive landscape, suppliers and distributors who will play a role in the process, and the larger business and cultural context. You can perform a 5C analysis as part of your GTM strategy to gain an understanding of opportunities and challenges in the market, but you can also apply it to craft an effective marketing and sales plan that stands out from the competition.
- CARE (Customers, Authenticity, Representation, Education): The CARE model is less common and was developed in this 2018 study on GTM strategies for start-ups launching e-innovations. “The findings of this study can be incorporated into a framework for start-ups involved in the launch of EIs — namely, the CARE framework,” the study reads. “The CARE framework relies on four pillars: customers, authenticity, representation, and education.” This framework adapts the service-marketing mix for the digital landscape and focuses on building strong customer relationships, maintaining a trustworthy brand presence, inclusively engaging a diverse audience, and empowering customers with knowledge.
Take a look at real-world examples of GTM strategies to see frameworks and processes in action.
How to Create an Effective GTM Strategy Step by Step
To create a GTM strategy, identify a target audience based on market research, determine a value proposition, and define marketing and sales tactics. Your approach to these steps depends on whether you employ a product-led or sales-led growth strategy.
1. Choose a Product-Led or Sales-Led GTM Strategy
The first step in a successful GTM strategy is to decide on the guiding principle for your sales and marketing plans. A product-led strategy is often the best choice for B2C and software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies with a simple user experience. A sales-led strategy works well for B2B companies with dynamic solutions, as it ensures that customers understand how to get the most out of the product.
Rex Huxford, Director of Demand Generation at MD Clarity, advises considering the particular strengths of your company and offerings. “Sales-led strategies focus on relationship-building to push customers to convert, while product-led strategies work by leveraging the product itself to pull customers to convert. Typically, sales-led works best when products are more complex, while intuitive or freemium product models better suit product-led strategies,” he says.
To make your decision, consider the different features of product-led and sales-led GTM strategies:
Product-Led GTM Strategy Elements | Sales-Led GTM Strategy Elements |
|---|---|
Product as main value proposition | Detailed, tailored value propositions |
Free trials and freemium models | Demos and webinars |
Inbound marketing | Account-based marketing |
Automated sales processes | Complex sales cycles |
Referral programs | Direct sales outreach |
Email nurturing sequences | High-touch lead nurturing |
Sales take place within product | Sales representative closes deal |
You can also create a hybrid strategy that borrows from both product-led and sales-led strategies to meet the needs of your specific product or market space.
In fact, the best strategy for your launch may be somewhere in-between, as Mandy Idol, Co-Founder and Chief Marketing Officer at Indigo Collective Group, suggests. “Both approaches have their merits, and the optimal GTM strategy depends on factors such as target market, competitive landscape, product complexity, and organizational strengths,” she says. “Finding the right balance between sales-led and product-led elements is key to achieving sustainable growth and market success.”
2. Analyze Market Research
It’s important to begin with data-backed insights that shed light on the competitive landscape, your customer demographics, and how your audience will relate to the new product or service. You might engage a third-party research group to gather data, or conduct surveys and focus groups to understand opportunities, pain points, and how to make your product stand out.
Laura Robison, the Founder and Marketing Consultant at GainKite, contends that research is the first step to understanding both your customer and your competitors. “You need to understand exactly what your customers need and build to that,” she advises. By analyzing the competitive landscape, you’ll also define “where your product fits into the marketplace and how it’s differentiated. You’ll need to do some competitor analysis to arrive at a market position that stands out from the noise,” she adds.
Consider using a competitive analysis template to organize your research and make sense of its takeaways.
3. Identify a Target Market and Create a Customer Profile
A clear target audience informs every element of your GTM strategy. Using the insights from your market research, create an ideal customer profile (ICP) to understand who has the buying power and how to reach them. Segment your market to reach specific customers, and develop detailed personas to concretize your insights.
“The ideal customer profile is arguably the most important part of your GTM strategy because if you get that profile wrong, every strategy and tactic built around it won’t align with real customer needs, pain points, and preferences,” Huxford says. “If you don’t know who the ideal customers are, you can’t possibly sell to them effectively.”
For general or product-led GTM strategies, a comprehensive customer profile template can help you evaluate your target audience and determine appropriate marketing tactics to reach individual buyers or users. For sales-led GTM strategies, there might be a more complex buying center made up of multiple decision-makers. It’s important to understand the role each individual plays, as well as their individual pain points, in order to strategize effectively. Use a B2B ideal customer profile template to develop your target business and profile the individuals within it.
4. Define a Value Proposition
In order to differentiate your product or service in the market, you need to develop a compelling value proposition. First, clearly articulate what makes your offering unique and why it is superior to competing solutions. Focus on the specific benefits that resonate most with your target audience, and ensure that your value proposition addresses real customer pain points and needs.
Consider not only the functional attributes of your product or service, but also the emotional rewards and broader impact it offers. Whether it will save time, reduce costs, improve efficiency, or enhance quality of life, your value proposition should be concise, specific, and powerful. Feature it prominently in marketing materials and sales pitches, and use it to form your core, customer-facing message about what sets your company apart.
Use a value proposition checklist to ensure you communicate the right benefits to your customers.
5. Map the Buyer’s Journey
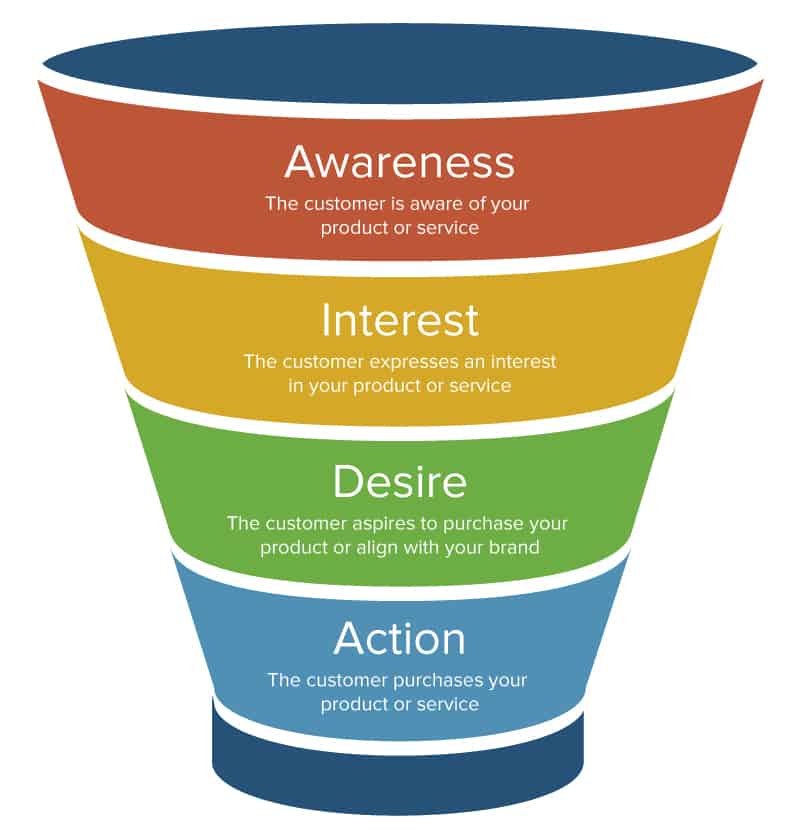
Map the buyer’s journey to understand which marketing and sales touchpoints to leverage. There are two main models used to illustrate the typical buyer’s journey: the funnel and the flywheel. The funnel is a more traditional approach that aligns best with a sales-led GTM strategy. The flywheel is a newer model that represents a product-led buyer’s journey.
The top of the sales funnel — Awareness — represents qualified leads who are aware of the product or service through marketing or sales efforts. At the middle of the funnel, in the Interest and Desire stages, the buyer has expressed interest and been in contact with a member of the sales team. Sales representatives aim to drive a conversion and move the buyer into the bottom of the funnel (Action).
While the funnel focuses on converting leads to customers, the flywheel model depicts a cyclical buyer’s journey that continues after a single sale. In the first phase, you attract potential customers to your product — with inbound marketing strategies, for example — and transition them from strangers to prospects. In the next phase, prospects engage with the product’s features and launch the sales process to convert them into customers. By delighting customers with your product’s features, you’ll turn them into promoters, who help you attract new prospects.
Elaine Chen, Founder of marketing consultancy Excogita, recommends the flywheel approach as a way to build long-term customers. “You shouldn't think of GTM as getting customers to make a one-time purchase, but rather starting an ongoing relationship with customers who will hopefully remain loyal over the years,” she says.
6. Develop Sales Strategies
The basic goal of any GTM strategy is to sell your product — and to do that, you need to consider all the facets of your sales process. Begin with a competitive pricing strategy, which could involve tiered pricing for different features. Determine a distribution strategy that covers where customers will find your product and make a purchase. Finally, decide on a sales process that aligns with your resources.
The four main GTM sales models are defined below:
- Self-Service Sales: With a self-service sales model, customers find and purchase a product on their own, either directly from the company or through a third-party retailer.
- Inside Sales: An inside sales model relies on a team of in-house sales representatives to nurture prospects and convert them into customers. Sales representatives typically use technology such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, email automation tools, and sales enablement platforms to nurture leads over a longer sales cycle.
- Field Sales: A field sales model employs a team of sales representatives who are assigned distinct geographic territories and interact directly with customers to drive conversions.
- Channel Sales: In a channel sales model, your company will partner with third parties to sell your product or service. The sales team focuses on stocking the product with distributors, resellers, agents, or other businesses, rather than selling directly to end customers.
In sales-led GTM strategies, inside sales and field sales are the most effective models. Representatives can align their sales process with the buyer’s journey to move prospects through the sales pipeline.
Product-led sales strategies should also align with the customer journey through the flywheel. The sales process must include the right tools to retain customers at each stage of the cycle — without direct contact from a sales representative.
7. Determine Marketing Channels
Decide what marketing channels will help you best reach your target audience. The right channels will depend on both your customer and your brand’s overarching marketing strategy. Use a
marketing strategy template
to develop a coherent marketing strategy for your brand and highlight specific channels for your GTM strategy.
Marketing is particularly important in a product-led GTM strategy, since it might be the way customers interact with your brand the most. Educational or content marketing helps users understand and get the most out of your product, while social media offers a place to engage with the brand personality and view success stories. Email marketing with automated nurturing sequences helps guide trial users to conversion.
With a sales-led GTM strategy, your marketing team might focus on supporting the sales efforts with account-based marketing (ABM) that resonates with specific prospects’ needs and pain points. Broader campaigns might use webinars, conferences, and live demos to introduce a new product or feature to the target audience.
Learn more about managing a marketing campaign — and the tools that can help you — in our comprehensive guide.
8. Align Stakeholders
A strong GTM strategy involves multiple teams across the company, from product development to customer support. Present your strategy to everyone who will be involved, so you can align stakeholders across marketing, sales, product, and customer support teams. Ask for feedback and fine-tune your strategy before putting it into action.
“When creating a GTM strategy, it's crucial to prioritize alignment between sales, marketing, and product teams to ensure seamless execution and consistent messaging,” Idol says.
“Your sales and customer support teams should feel both prepared and excited for your launch,” Robison adds. “Don’t put them in a position where they’re learning things from customers and have to respond flat-footed. Build anticipation internally and educate your teams so that they can influence success.”
Consider using a GTM strategy presentation template to streamline your strategy to present it clearly and focus on the high-level elements.
9. Run Tests to Optimize Strategies
Before you execute your GTM strategy on a large scale, run tests using online surveys, focus groups, or A/B testing with segmented targeting to ensure your message will reach your audience. Consider testing versions of your value proposition, marketing channels, or product features. Collect data on which channels and messages are most effective in converting your target audience, so you can adapt if necessary before writing your GTM plan.
“Make sure to include testing and optimization as part of your strategy,” Chen says. “Things will never go exactly as expected even with the best GTM plan, and you need to retain flexibility so you can continue to grow and improve.”
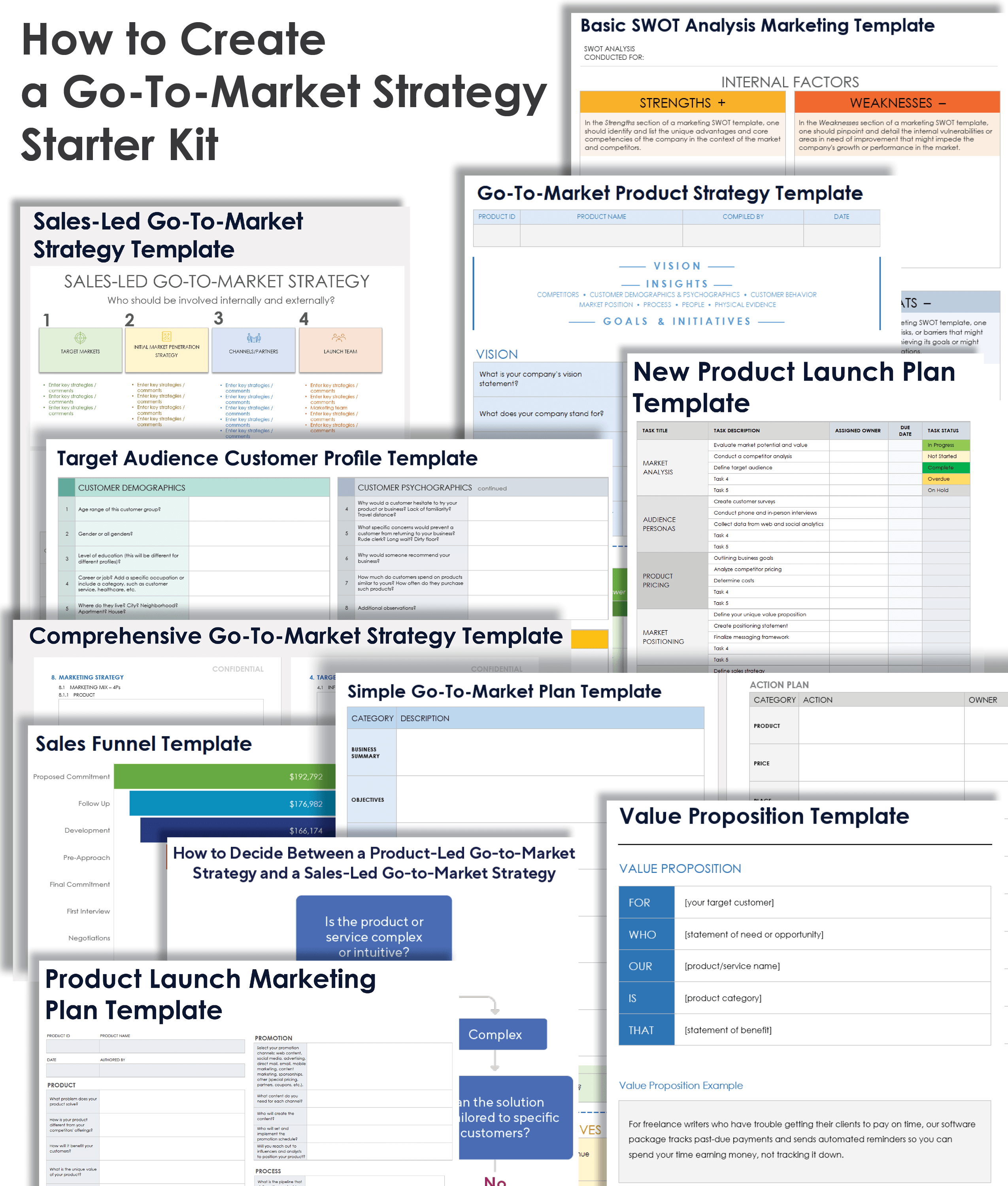
GTM Strategy Starter Kit
Download GTM Strategy Starter Kit
Use this free starter kit to help you create your GTM strategy. This free, downloadable file includes essential tools for situational analysis and audience development, as well as templates for general, sales-led, and product-led GTM strategies.
In this kit, you’ll find:
- A comprehensive GTM strategy template in Microsoft Word with sections for each element of your GTM strategy.
- A GTM product strategy template in Excel to help you implement a product-led strategy with a focus on the features that will set your product apart.
- A sales-led GTM strategy template in PowerPoint to help you align your sales team on the target market, value, and channel partners in your market penetration strategy.
- A target audience customer profile template in Microsoft Word to help you develop your understanding of your customer demographics and behaviors.
- A strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats (SWOT) analysis template in Microsoft Word to help you evaluate your market position.
- A value proposition template in Microsoft Word to help you develop targeted messaging.
- A sales funnel template in Excel to help you fine-tune your sales process.
- A product launch marketing plan template in Excel to help you finalize your marketing mix using the 7Ps.
- A new product launch plan in Excel that breaks down the steps from pre-launch strategies through post-launch evaluation.
- A GTM plan template in Microsoft Word to help you execute your strategy with a clear action plan.
How to Use Generative AI to Strengthen Your GTM Strategy
Advancements in generative AI have made it a powerful tool for developing robust GTM strategies. Use AI to assist with analyzing your market research data and competitors, develop customer profiles, and more.
Taylor Radey, founder of Randall Pine, has more than 15 years of experience helping businesses with digital transformation. Alongside more specific ideas for GTM strategy, she highlights the importance of general AI best practices, such as removing personal information or sensitive data, reviewing the output for inaccuracies or biases, and providing as much detail and specifics as possible to get the most helpful results.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the ways AI can assist with GTM strategy:
- Analyze Customer Sentiments: AI can help you analyze customer-provided information — such as reviews or other feedback — to better understand your audience’s relationship to your product. “Aggregate customer reviews, social media posts, and support tickets, and then ask ChatGPT to analyze the sentiment,” Radey advises. “You might ask it to categorize sentiments as positive, negative, or neutral; to summarize the key themes; or to highlight commonly used language. Large language models (LLMs) are excellent at parsing natural language and can help you analyze this customer data in new ways.”
- Prepare and Run A/B Tests: Aside from language models such as ChatGPT, AI powers tools to help marketing and sales teams predict the success of their messaging. “With an AI testing tool, we can run multiple tests across many variables simultaneously for fast, reliable results,” Huxford says. “We have a better idea of what messaging customers will respond to before we launch, so we can make the right waves and maximize audience impact from day one.” Even without advanced tools, ChatGPT can help you refine your messaging. “While you can’t run A/B tests using ChatGPT, you can feed existing messages into ChatGPT and ask for variations or improvements,” Radey adds. “This can help you generate dozens of iterations and fresh ideas for A/B testing.”
- Draft Buyer Personas: LLMs are especially useful for summarizing and synthesizing information. “By inputting known data about your customer segments, you can ask ChatGPT to craft detailed narratives that represent each persona,” Radey says. “This might include existing buyer persona profiles, CRM notes, customer feedback, call transcripts, and more.”
- Gain a Fresh Approach to Data: Radey also suggests using AI to consider new angles in your data, beyond a basic analysis. “For example, you might input a data set and ask: ‘What else should I be thinking about? How could I enrich this data set? What questions could I ask about this data that would lead to interesting strategic insights? What are some creative ways we could visualize this data?’”
How to Write a Go-to-Market Plan Step by Step
A go-to-market plan includes key information about the product or service, insights from market research, the buyer’s journey breakdown, marketing campaign roadmaps, sales strategies, and KPIs. An effective GTM plan becomes the single source of truth for your launch.
1. Gather Information and Input
Before you start writing your GTM plan, you need to develop a clear GTM strategy using market research and data analysis, and collaborating with stakeholders on the product and sales teams. Gather all the relevant information — such as product specifications, A/B test results, and audience demographics — and review with stakeholders to ensure your strategy aligns with the overarching business objectives.
2. Use a Template
Templates such as this simple GTM marketing plan template help you organize your strategy clearly, ensure you are covering all the necessary bases for a comprehensive GTM plan, and communicate with stakeholders and collaborators.
3. Write a Mission Statement
Set the tone for your launch plan by introducing the larger purpose behind your brand and product. Include customer pain points and explain how this product will solve them, as well as how it fits within the larger brand identity or offerings.
Learn more about how to write an effective mission statement.
4. Perform a Situational Analysis
Organize your market research data into a structured situational analysis in order to highlight relevant insights. Your situational analysis could take the form of a SWOT analysis, a 5C analysis, a competitive analysis, or other formats.
Consider using an industry analysis template to streamline your research so you can identify the opportunities and threats associated with bringing the new product to market.
5. Define Goals
Your GTM plan should include specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals so that you can direct your efforts and evaluate your success. Consider setting individual marketing and sales goals, and ensure they are in line with your overarching business objectives. Marketing goals might focus on the number of impressions or marketing qualified leads (MQLs), while sales goals often center on conversion and retention rates.
Learn more in this definitive guide to writing SMART goals.
6. Describe Your Target Market
Using the insights developed in your GTM strategy about your audience and ideal customer, finalize your detailed buyer persona with demographic, psychographic, and behavioral data. Analyze insights about the customer’s relationship to the brand, and address specific pain points that this product or service will alleviate. Develop personalized messages for each customer profile, so you reach each one with messaging that resonates.
7. Lay Out Marketing and Sales Tactics
A successful GTM plan hinges on its ability to convert your marketing and sales strategies into actionable campaigns and processes. Break down your customer’s buying cycle to determine the ideal marketing and sales touchpoints. Create a sales cycle and pipeline that aligns with your buyer’s journey. Highlight your market-tested unique selling proposition and detail a marketing mix (4Ps) that corresponds with your pricing and distribution sales strategies. Provide specific marketing campaign tactics for each channel and message.
Discover a collection of sales plan templates to help you forecast and plan your sales process effectively.
8. Determine Performance Metrics
Decide how you will measure the success of your launch, which key benchmarks to consider, and when to revisit and adjust your plan based on customer feedback. Choose metrics that align with your goals and define your data collection methods and frequency.
For example, you might measure your customer acquisition cost (CAC), which includes the total marketing and sales expenses involved in converting a new customer. You can compare your results to benchmarks from past launches or industry standards, and aim to reduce CAC as efficiencies improve. If your plan follows a sales-led strategy, consider tracking the time to close, or the average amount of time it takes between first contact and conversion. For product-led strategies, you might focus on product usage metrics and market share.
9. Create a Budget and Action Plan
In order to execute your strategy, you need to appropriately allocate resources and have a timeline for accomplishing each component of your plan. Create a clear action plan with team member responsibilities and deadlines for each task. Break down the phases of your plan into pre-launch, launch, and post-launch, and develop a budget that aligns with your marketing and sales plans for each phase. A budget is also essential for evaluating your ROI.
“GTM planning shouldn't stop after the initial launch announcement,” Chen advises. “A phased approach that builds awareness, interest, and then desire to purchase over time will be critical to driving sales. Instead of staking everything on an initial splash, allocate marketing budgets over this entire period.”
How to Use Generative AI to Strengthen Your GTM Plan
Generative AI is an effective tool for nailing down the specifics of a GTM plan. It can help you develop your budget, draft content, and brainstorm campaigns.
Here are some tips on using generative AI to write a stronger GTM plan:
- Make Data-Driven Decisions for Better Budget Allocation: Use AI to analyze data and make informed budgeting decisions. “AI is helping us set better GTM budgets from the start,” Huxford says. “By quickly analyzing historical market data, market size, competitors, and company performance, we can allocate budgets for different channels and optimize our spending.”
- Role-Play with Buyer Personas: AI is a great tool for brainstorming ways to reach your ideal customer. Ask the AI to play your customer and give it as many details as possible. “Include your buyer persona profile to set the stage with the target customer’s job title, pain points, and motivations,” Radey suggests. “Then, ask it questions. This can help you dig deeper into customer expectations, discover challenges and pain points you might not have considered, and uncover new ideas for content and campaigns that might resonate with this audience.”
- Personalize Messaging: Similarly, AI can help you tailor your messaging for different channels and audiences. “Provide ChatGPT with descriptions of your buyer personas and the core message or value proposition. It can then help draft personalized marketing messages, from emails to social media posts, that resonate with each persona,” Radey says.
Successfully Launch Your Go-to-Market Strategy with Smartsheet
The best marketing teams know the importance of effective campaign management, consistent creative operations, and powerful event logistics -- and Smartsheet helps you deliver on all three so you can be more effective and achieve more.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.